July 25, 2023
In Singapore, domestic politics are famously boring. The tiny yet ultra-prosperous nation, which has been ruled by the People’s Action Party since independence in 1965, is not just a physical island but also an island of political stability surrounded by volatile neighbors.
PAP officials are themselves notorious for being competent, honest … and such wholesome squares that, well, no one really talks about them. Not anymore.
Singapore has been rocked this month by three political scandals that have shown that not all its politicians are as squeaky clean as their reputation.
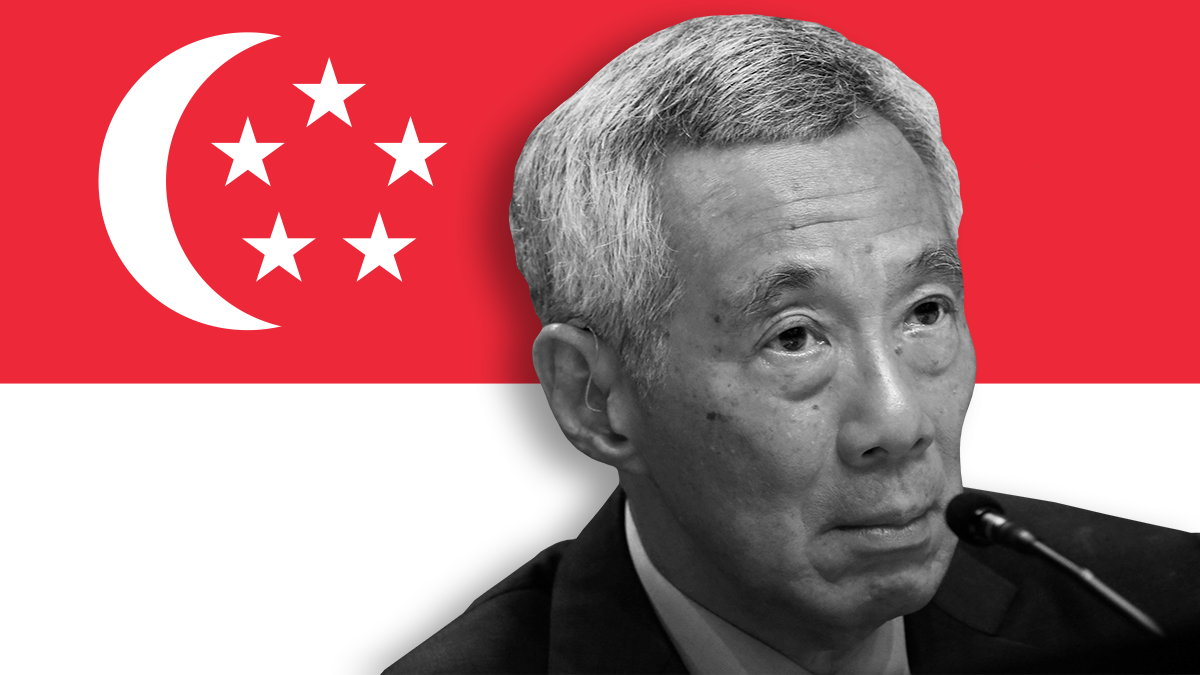
On Tuesday, the government of Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong invoked a draconian fake news law to mandate that Lee's estranged brother "correct" a Facebook post in which he claimed that the state had paid for renovations in two high-end bungalows rented by senior cabinet officials. Lee Hsien Yang insists that what he wrote is true and has yet to comply with the order.
But wait, there's more! Last week, two PAP officials — the speaker of parliament and an MP — stepped down for having an "inappropriate relationship" in defiance of PM Lee's orders to end the romance. And in early July, a senior minister was arrested along with a prominent tycoon in Singapore's most serious corruption probe in decades.
Okay, the corruption stuff is a big deal — especially in the fifth least corrupt country in the world, according to Transparency International. But the Lee family feud and the parliamentary fling would barely have raised eyebrows anywhere else. So, why all the fuss?
Singapore has long pitched an image of a clean, graft-free government to lure foreign investors. It has paid off: The city-state of only 5.5 million people is now considered Asia's top financial hub, especially after China's crackdown in Hong Kong.
The PAP has always justified its benevolent dictatorship by holding its members to extremely high standards. But that moral high ground is now being tested ahead of a much-awaited power transition away from the Lee dynasty. (Singapore was founded by Lee Kuan Yew, father of the current PM, and regarded as one of Asia's most influential statesmen until his death in 2015.)
The junior Lee's handpicked successor is his deputy Lawrence Wong, the PAP's idea of a “personable” leader: He grew up in public housing, didn’t attend elite private schools, plays guitar, shows (some) emotion on Instagram, and is divorced without kids in a socially conservative nation. Otherwise, he's another PAP goody two-shoes.
The PM isn't required to call an election and doesn’t plan to hand over power to Wong until 2025. Although that'll be the first time no member of the Lee family will be running for office, the ruling party probably won't get voted out of power because the opposition is weak and bankrupt — thanks in part to public defamation lawsuits that government lawyers always win.
Still, the recent scandals have demonstrated that the PAP is not infallible and that its members are capable of sin. With the genie now out of the bottle, don't be surprised if more Singaporeans eventually feel the urge to do something unthinkable: vote for someone else.From Your Site Articles
More For You
Two weeks ago, President Donald Trump launched a war of choice to topple Iran's regime expecting a quick, clean win.
Most Popular
What's Good Wednesdays
What’s Good Wednesdays™ -Oscars Edition
Sponsored posts
Investing in skills. Strengthening communities.
Walmart sponsored posts
Walmart’s $1 billion investment is strengthening associate careers
Last week, Microsoft, Europol, and industry partners took coordinated action to disrupt Tycoon 2FA, a major phishing‑as‑a‑service operation designed to bypass multifactor authentication. Active since 2023, the service fueled large‑scale online impersonation, enabling fraud, data theft, and disruptions across sectors, including healthcare and education. Acting under a US court order, the coalition seized hundreds of domains that powered Tycoon 2FA’s infrastructure — underscoring the need for global, public‑private cooperation to counter industrialized cybercrime and protect digital trust. Read the full blog here.
Australian mining giant Lynas will sell rare earths to Japan for 12 years in a major pact meant to chip away at China’s dominance of the global market.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.