April 28, 2020
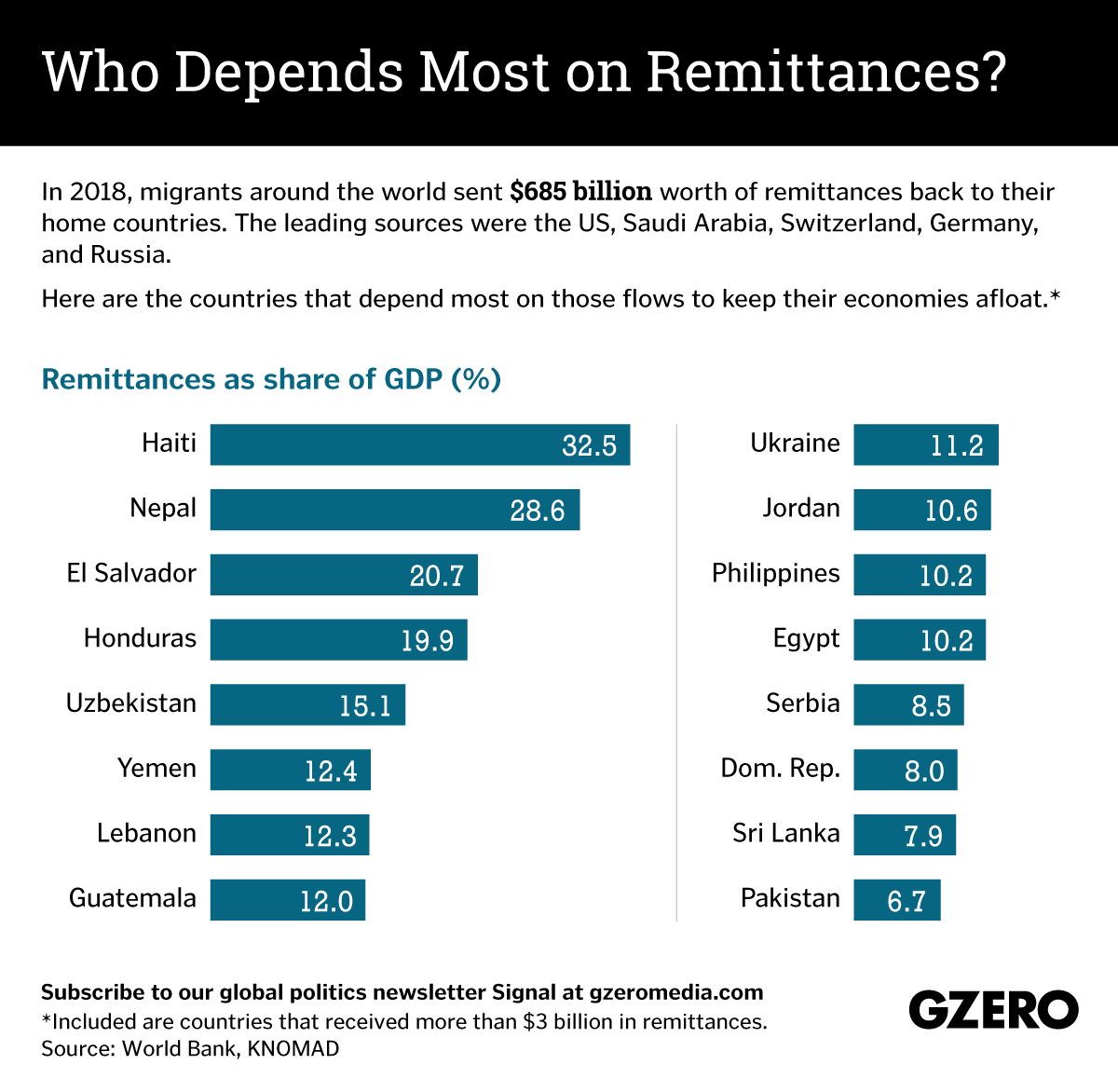
Around the world, hundreds of millions of households and families depend on remittances sent home by migrants working abroad. For many nations, those flows form a sizable chunk of the national economy. But the World Bank has now warned that coronavirus-related lockdowns could slash remittances by as much as 20 percent this year, wreaking havoc on the economies that depend on that cash the most. Consider Haiti, the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, where remittances account for almost a third of GDP. Or Central American countries like El Salvador and Honduras where the figure is roughly 20 percent. Tiny Lebanon's giant diaspora sends home cash worth 12 percent of GDP, while transfers from Philippine seamen and overseas domestic workers support 10 percent of their home economy. Here's a look at some of the countries that will be hit hardest if global remittance flows grind to a halt because of the coronavirus pandemic.
More For You
- YouTube
What is President Trump trying to achieve in Iran, and how does his strategy compare to past US interventions in the Middle East?
Most Popular
Think you know what's going on around the world? Here's your chance to prove it.
President Donald Trump delivers remarks at the White House AI Summit at Andrew W. Mellon Auditorium in Washington, D.C., Wednesday, July 23, 2025.
Joyce N. Boghosian/White House/ZUMA Press Wire
The 2024 US presidential campaign season may have been the first time voters had to contend with AI during an election, confronting deepfakes of Taylor Swift vowing support for Donald Trump and AI robo-calls of Joe Biden telling voters not to cast their ballots.
- YouTube
Donald Trump is polling underwater on the economy in a critical midterm election year. What can he do to change voters’ perceptions?
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.