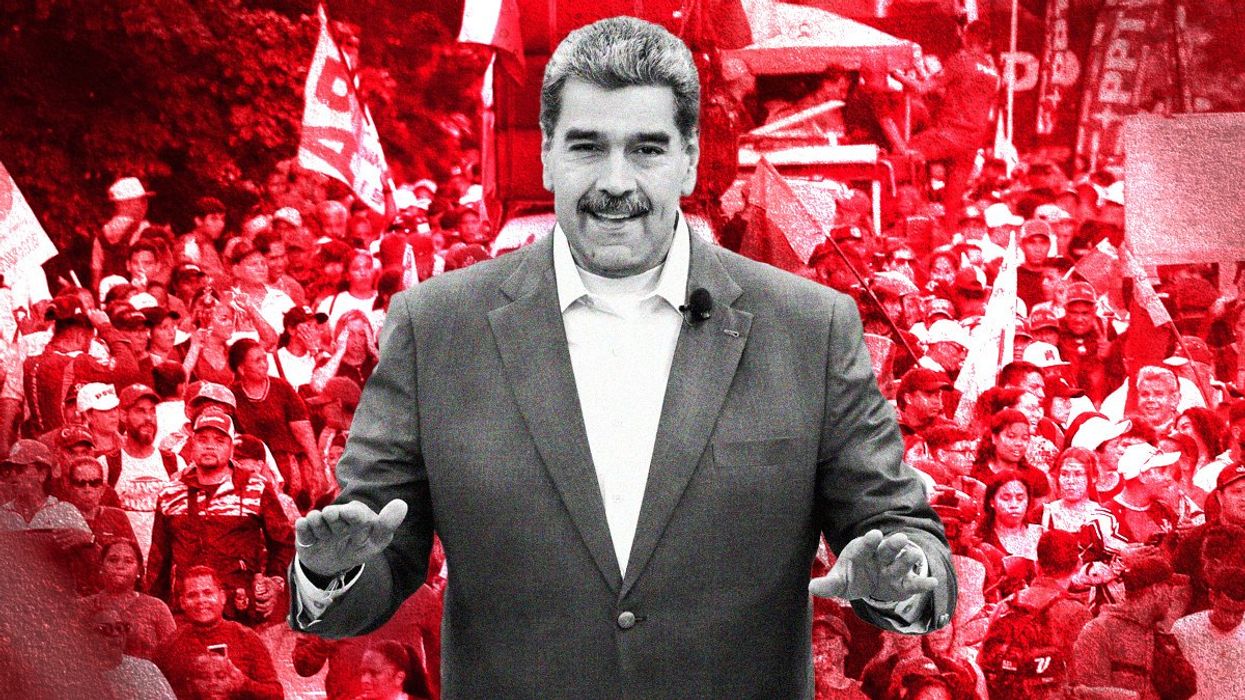
Earlier this week, the US Justice Department seized the airplane used by Venezuelan strongman Nicolás Maduro, his equivalent of Air Force One. It’s the latest signal that the Biden administration remains furious at Maduro for stealing another of his country’s elections — and that it needs some way of expressing that anger. Will this latest US move undermine Maduro’s hold on power? Don’t hold your breath.
Background: US presidents have tried for years to force Maduro, in power since 2013, to hold free and fair national elections in Venezuela. Maduro has refused because he knows he would lose any contest that isn’t rigged in his favor. In 2018’s presidential election, he manipulated the vote to a degree that made international headlines, and the US and more than 50 other countries recognized the president of the National Assembly, opposition leader Juan Guaidó, as the country’s rightful leader. It made no difference; Maduro pressed on and remained in power.
Under President Donald Trump in March 2020, the US Justice Department charged Maduro and 14 of his political allies with narco-terrorism, drug trafficking, and corruption in hopes of loosening his grip. No dice.
The Biden administration has tried a different approach. Ahead of this year’s presidential election in Venezuela, the US lifted some sanctions in hopes of persuading Maduro to change his mind — and of keeping US election-year gasoline prices down. This can charitably be called the triumph of hope over experience. In January, the US was forced to reimpose some previous sanctions after Maduro barred the country’s most popular opposition candidate, Maria Corina Machado, from running against him this year.
Machado then elevated a little-known official, Edmundo González, to run against Maduro in her place. The presidential election went ahead in July, and Maduro immediately declared victory … without releasing any voting data. Venezuela’s opposition has since published more than 80% of the information printed and collected from the country’s voting machines thus far to make the case that González soundly defeated Maduro. In response, just as he did with Guaidó in the past, Maduro now appears ready to arrest González, or at least to use the threat of arrest to force González to flee the country. To show just how much power he still commands, Maduro decreed this week that this year’s celebration of Christmas will begin on Oct. 1. Seriously.
The US and Venezuela’s neighbors, particularly Colombia, have a clear interest in restoring credibility to Venezuela’s politics, in part because both countries and the region have absorbed millions of refugees fleeing political repression or simply looking for brighter economic prospects than Venezuela’s basket-case, sanction-plagued economy can provide.
The US request that the Dominican Republic seize Maduro’s plane is just the latest example of ineffectual pressure. US Attorney General Merrick Garland has claimed the aircraft “was illegally purchased for $13 million through a shell company and smuggled out of the United States for use by Nicolás Maduro and his cronies.” A US official told CNN this week that Washington is “sending a clear message here that no one is above the law, no one is above the reach of US sanctions.”
Let’s cut the chase: Maduro will continue to resist any deal that pushes him from power. The US has reportedly offered him amnesty if he agrees to step down. Some in Congress want a return to the Trump administration’s tougher approach. A group of bipartisan lawmakers led by Sens. Jim Risch (R-ID), Rick Scott (R-FL), and Bill Cassidy (R-LA) appear ready to present the so-called “VALOR Act,” a bill co-sponsored by Democrats including Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-FL) and Sen. Michael Bennet (D-CO). The bill would significantly ratchet up US sanctions against Venezuela.
Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico have also tried to pressure Maduro by calling for the release of detailed voter tallies and an election audit conducted by some institution other than Venezuela’s Supreme Court, which remains fully under Maduro’s thumb.
But the Venezuelan leader still has firm backing from the country’s military and security forces, which profit from his rule. They will also again become the target of sanctions, but they’ve weathered these storms before and have had plenty of time to prepare for one of this year’s least surprising storms. In fact, Maduro has responded to pressure from the US and other governments not by offering concessions but by arresting opposition leaders and restricting access in Venezuela to social media that can be used to organize protests.
To date, the Trump get-tough approach and the Biden engagement strategy have both failed, because the US is no better able to dislodge Maduro than they were to sweep away Cuba’s Fidel Castro. Maduro, like Castro, has friends in Beijing and Moscow ready to provide diplomatic cover and just enough cash to render US leverage useless. Until there is a revolt from within Maduro’s domestic alliance of backers, clients, and enablers, the strongman will remain strong.