Trending Now
We have updated our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use for Eurasia Group and its affiliates, including GZERO Media, to clarify the types of data we collect, how we collect it, how we use data and with whom we share data. By using our website you consent to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy, including the transfer of your personal data to the United States from your country of residence, and our use of cookies described in our Cookie Policy.
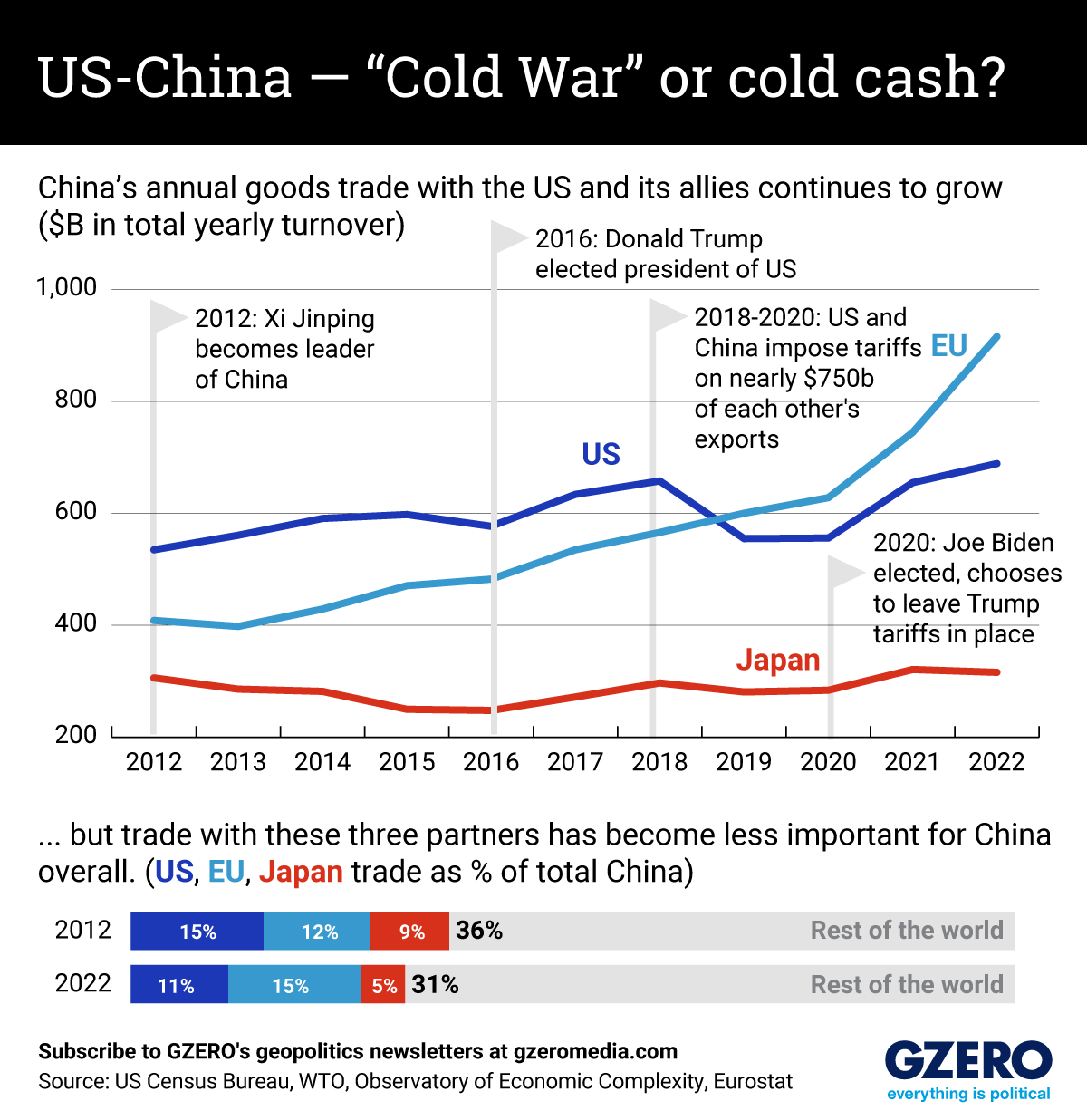
In the 10 years since Xi Jinping took power as China’s leader, trade volumes between the world’s top two economies have continued to grow. The same is true of Chinese trade with key US allies like the EU and, to a lesser extent, Japan.
In fact, US-China trade has continued to rise despite the Great US-China Trade War of 2018-2020, when the Trump administration and Beijing slapped tariffs on some $730 billion of each other’s goods. In 2022, US-China trade reached a dizzying record high of $689 billion. For comparison with the actual Cold War — US-Soviet trade throughout the entire 1980s amounted to less than $50 billion.
That said, while overall trade continues to rise between China on one side and the US and its allies on the other, this trade is steadily becoming less important as a part of China’s overall global commerce. That is, China is relying ever more on trade with the rest of the world, and less on Uncle Sam and friends.
To show what that looks like, we track China’s trade with the US, EU, and Japan, and look at how that has figured into China’s total trade between 2012 and now.
A Cold War may come one day, but for now, cold cash is still king.