Trending Now
We have updated our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use for Eurasia Group and its affiliates, including GZERO Media, to clarify the types of data we collect, how we collect it, how we use data and with whom we share data. By using our website you consent to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy, including the transfer of your personal data to the United States from your country of residence, and our use of cookies described in our Cookie Policy.

In recent years global supply chains have gotten badly kinked by resurgent protectionism, the economic havoc of the pandemic, deepening rifts between the US and authoritarian countries, and the war in Ukraine. The result is inflation levels not seen in advanced economies since the 1980s and a food security crisis of global proportions.
In this special edition of Signal, we’ll ask what comes next by surveying the scarcities, tracking the travails of truckers, scarfing down a handful of (micro)chips, and asking whether “friends” can really save the day. Enjoy!
- The Signal Team
Can you get by with a little help from your friends?
 Alex Kliment
Alex KlimentThe pandemic inflicted a huge shock on supply chains, but there is another force at work remapping global trade flows too: the deepening ideological divide between the US and China, framed in Washington as a broader competition between democracies and autocracies.
The so-called “de-coupling” between the world’s two largest economies began during the presidency of Donald Trump, who slapped tariffs on China in a largely unsuccessful attempt to address the real harms that offshoring has done to some US workers.
But now, as global trade reorients itself in the wake of the pandemic, Washington is making a broader push for US companies to source their goods from factories in friendly democracies rather than authoritarian countries — China, Russia, and the gang — that could use their control over key materials or products to inflict pain on the West. Russia’s use of oil and gas to pressure Europe is one clear example, of course, but there are others: China’s monopoly on the production of rare earths used for electronics, or the precarious concentration of global microchip production in Taiwan, which lives under the constant threat of Chinese invasion.
US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen recently touted the benefits of so-called “friendshoring” on a visit to South Korea, which is trying to lure American supply chains away from China and to start making more microchips itself. Southeast Asian manufacturing powerhouses like Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia are also keen to continue capitalizing as “friends” of the US.
Friendshoring may offer certain protections in a world of deepening ideological competition, but there are tradeoffs: “friendly” countries may not always produce goods as cheaply or efficiently, meaning that consumers may have to accept higher prices, particularly in the short term. Is the tradeoff of greater security in exchange for less efficiency worth it? More to the point, is it now unavoidable?
Shortages reach far beyond food
 Willis Sparks
Willis SparksThe war in Ukraine is just the latest crisis to befall global supply chains in recent years, and it appears likely to get worse before it finally eases. It’s not just about interrupted flows, shortages, and higher prices for food and fuel. According to a report published in May 2022 by Dun & Bradstreet, a total of at least 615,000 businesses operating globally depend on supplies from either Russia or Ukraine. About 90% of those firms are based in the United States, but supply chains in Europe, China, Canada, Australia, and Brazil are heavily impacted. According to the report, a total of 25 countries have a high dependency on Russia and Ukraine for a variety of commodities.
Five months into the war, it’s clear that the likeliest outcome of the current fighting will be a long-term stalemate. Russia doesn’t appear militarily strong enough to take and hold all of Ukraine, and Ukraine doesn’t appear strong enough to drive Russian troops completely off Ukrainian land. As a result, those who depend on resources and production inputs from Russia and Ukraine now know they’ll likely need to invest in new suppliers of hundreds of different commodities and products – from sunflower seeds to turbojets – to build better resilience into their supply chains, rather than simply waiting for the fighting to end.
CIO Strategy Webcast Series
 Citi Private Bank
Citi Private BankJoin us each week on Thursday at 11:30 am EST for a conversation with senior investment professionals and external thought leaders on timely market events and ask your most pressing questions.
The Graphic Truth
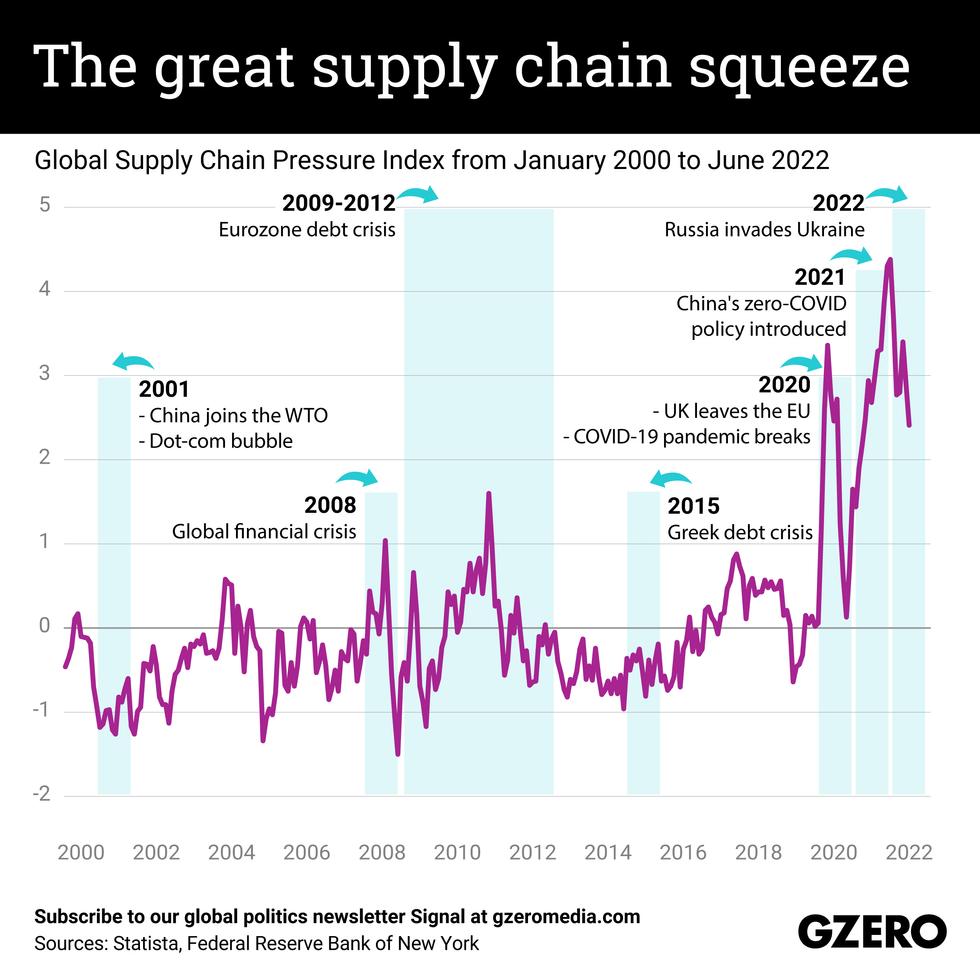 Luisa Vieira
Luisa VieiraThe pandemic sent global supply chains into a tizzy. Then, just as economies were embarking on their post-COVID economic recoveries, Russia invaded Ukraine, upending the global grain trade and sending supply chains spiraling further. Supply chain frictions have a lot of unintended consequences: Brexit-related supply chain issues made it hard for some Brits to get their hands on a pint of beer, while China’s punitive zero-COVID policy drove the auto industry – among others – into a full-blown crisis. We take a look at the Global Supply Chain Index from 2000-2022 along with key global economic milestones.
What We're Watching: Truckers wanted & not-so-cheap chips
 Gabrielle Debinski
Gabrielle DebinskiWhere are all the truck drivers?
The global truck driver shortage has been disrupting already-out-of-whack supply chains, particularly in the US, the European Union, and Britain – further complicating their post-pandemic economic recoveries. Last year, the American Truckers Association said it was around 80,000 drivers short, while in Europe, a deficit of 40,000 truckers has contributed to long waits and empty shelves. What’s going on? The pandemic has upended the way we work. Trucking is an arduous and ungratifying gig: Drivers often spend days or weeks far away from home, and they don’t get paid for hours spent waiting for goods to be loaded and unloaded. The road can be grueling, the compensation is underwhelming, and the benefits are often … nonexistent. In the US, trucking salaries have plunged in recent decades. Median wages for truck drivers in 1980 were about $110,000 annually (adjusted for inflation); in 2020, they were just $47,130. Unsurprisingly, many truckers are opting for jobs with better conditions and pay, so trucking firms in Europe and the US are struggling to lure drivers back to work and recruit new staff. It’s particularly grim in the UK, where supply-side frictions have been exacerbated by Brexit. In the US, meanwhile, companies like Walmart are fighting back by offering massive salary hikes to attract truck drivers. Will it get the wheels turning?
Chipping away at supply chains
The US Congress this week passed the behemoth Chips and Science Act, which ponies up $52 billion in subsidies and incentives to boost domestic production of semiconductors, the invisibly thin microchips that are essential for everything from phones, cars, and factories, to fighter jets, cruise missiles, and artificial intelligence. With the bill, Congress is making a big move in a new global “Chips race” for dominance of the industry: the EU is now spending close to $50 billion on the same thing, and China, which still depends on the US and its allies for inputs into its home-grown chips, has poured hundreds of billions into someday becoming a semiconductor superpower itself. For all three of the world’s largest economies, the concern is the same: the semiconductor market is highly concentrated, particularly in Taiwan, which produces more than 60% of the world’s chips. That’s a problem commercially – in 2021, there was a global shortage after tech firms gobbled up the entire supply, leaving automakers scrambling for chips. But it’s also a problem geopolitically. China doesn’t want to be dependent on chips from a Taiwan that’s allied with the US, while the US and EU don’t want to rely on a Taiwan that could be taken over by China any year now. Critics of the Chips act say its a sop to powerful tech companies that can well afford to build their own factories, and there are questions about whether the money will be spent on the right things: making the chips is one thing, cutting edge R&D is a whole other bowl of chips, and the supply chain for a single chip can pass through many countries before final assembly. As a cautionary tale: the EU aimed in 2013 to double its share of global semiconductor production to 20% by 2020. It didn’t work.
Future-proofing: How we fix broken supply chains
“Envision supply chains like a strand of Christmas lights. If one light goes out, then the whole strand will stop working.” So says Eurasia Group’s Christina Huguet on the latest episode of the Living Beyond Borders podcast, which focuses on the moments those lights went out: when the pandemic hit shipping, manufacturing, and labor all at once. Huguet, along with moderator Shari Friedman, Eurasia Group’s Managing Director of Climate and Sustainability, and David Bailin, Chief Investment Officer and Global Head of Investments at Citi Global Wealth, look at what it will take more than two years later to turn those lights back on and create more resilient global supply chains.
Listen here.
Hard Numbers: The scarcity edition
 Gabrielle Debinski
Gabrielle Debinski2 million: As the war in Ukraine rages on, the African continent is facing a shortfall of around 2 million metric tons of fertilizer that’s causing an unprecedented loss in food production throughout the continent. A Senegalese official warned at a recent G20 meeting that starvation could kill more Africans than COVID-19.
10: American women are the latest victims of the supply chain crunch. Tampon shortages as a result of staffing issues at manufacturing plants, transportation disruptions, and the scarcity of materials like cotton caused tampon prices to soar almost 10% in the US in recent months.
50: Europe’s largest paper packaging company, Smurfit Kappa, recorded a whopping 50% increase in core profit during the first half of this year as a result of surging pandemic-related demand. Still, the company says it’s preparing for paper shortages across the continent in the months ahead as a result of mandatory gas rationing as EU states try to reduce their dependence on Russian natural gas.
10: Several Polish supermarkets are limiting sugar purchases to 10 kilograms per person after consumers cleared out shelves fearing further price hikes and scarcity of the sweet staple. Poland, one of Europe’s biggest sugar producers with ample supply of the stuff, recently recorded its highest inflation rate in 25 years.This edition of Signal was written by Beatrice Catena, Gabrielle Debinski, Alex Kliment, Carlos Santamaria, and Willis Sparks. Edited by Tracy Moran. Graphic by Luisa Vieria. Art by Paige Fusco.