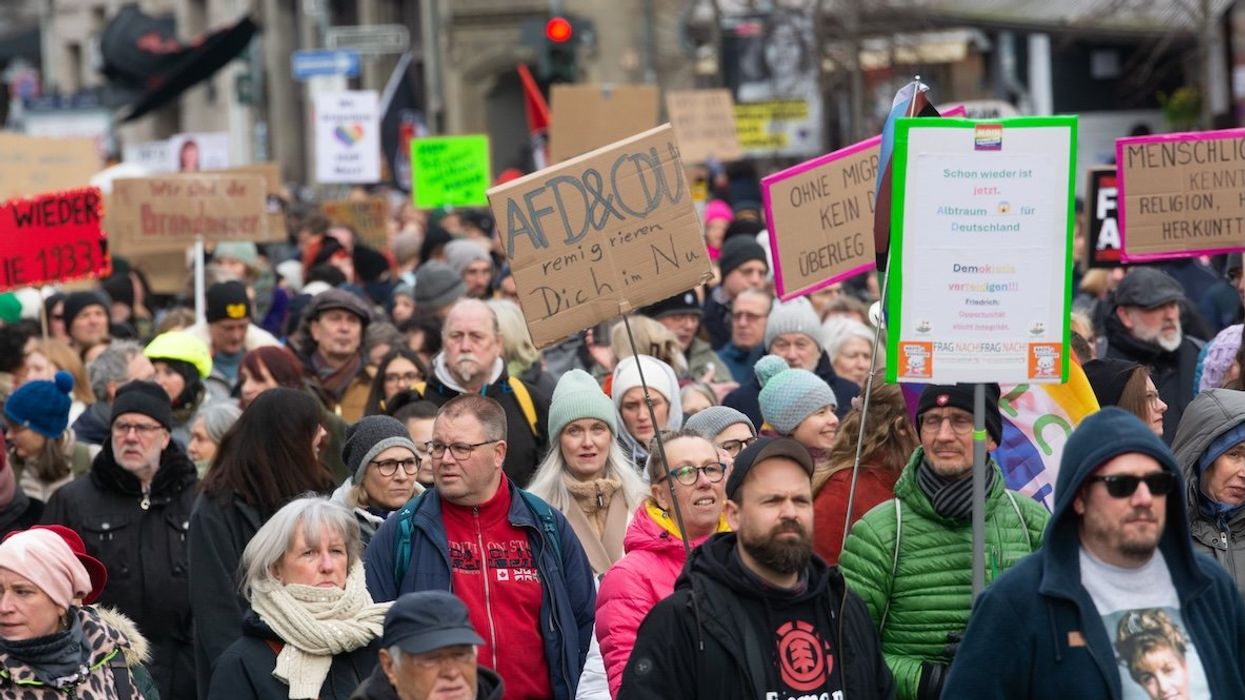What We're Watching
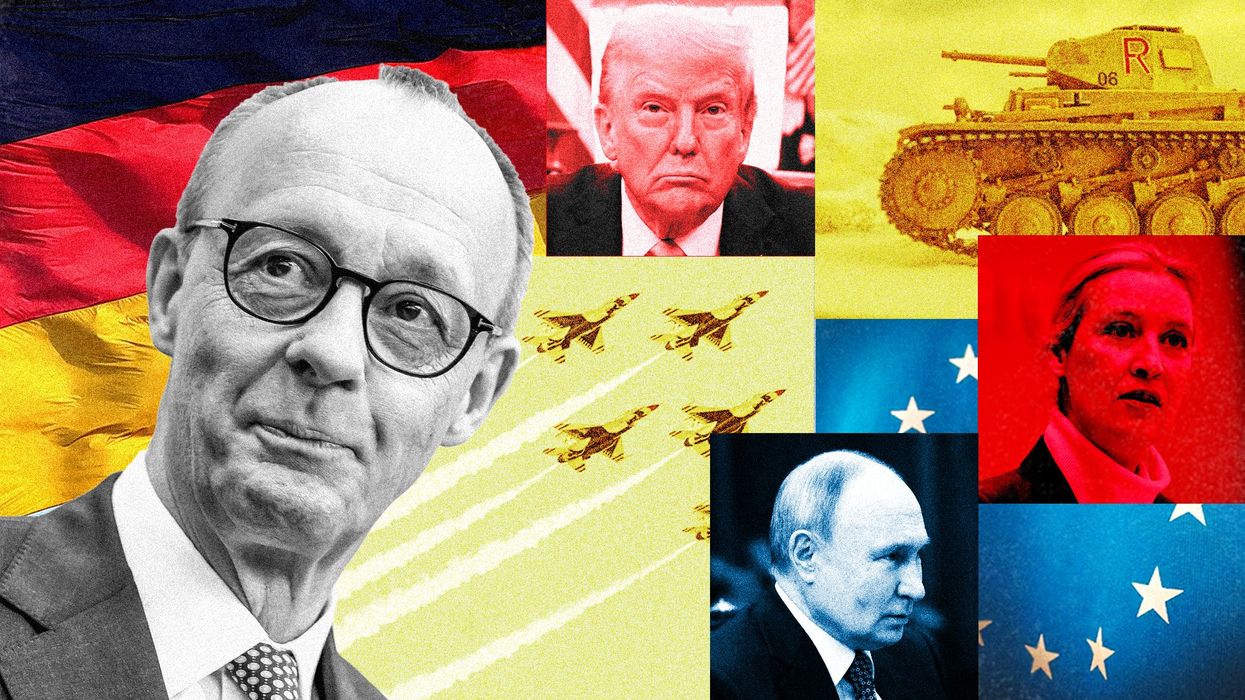
Germany’s Friedrich Merz strikes grand coalition deal
Germany’s leading establishment parties reached a grand coalition deal on Wednesday, bringing Europe’s largest economy a step closer to having a formal government amid severe domestic and global challenges.
Apr 09, 2025