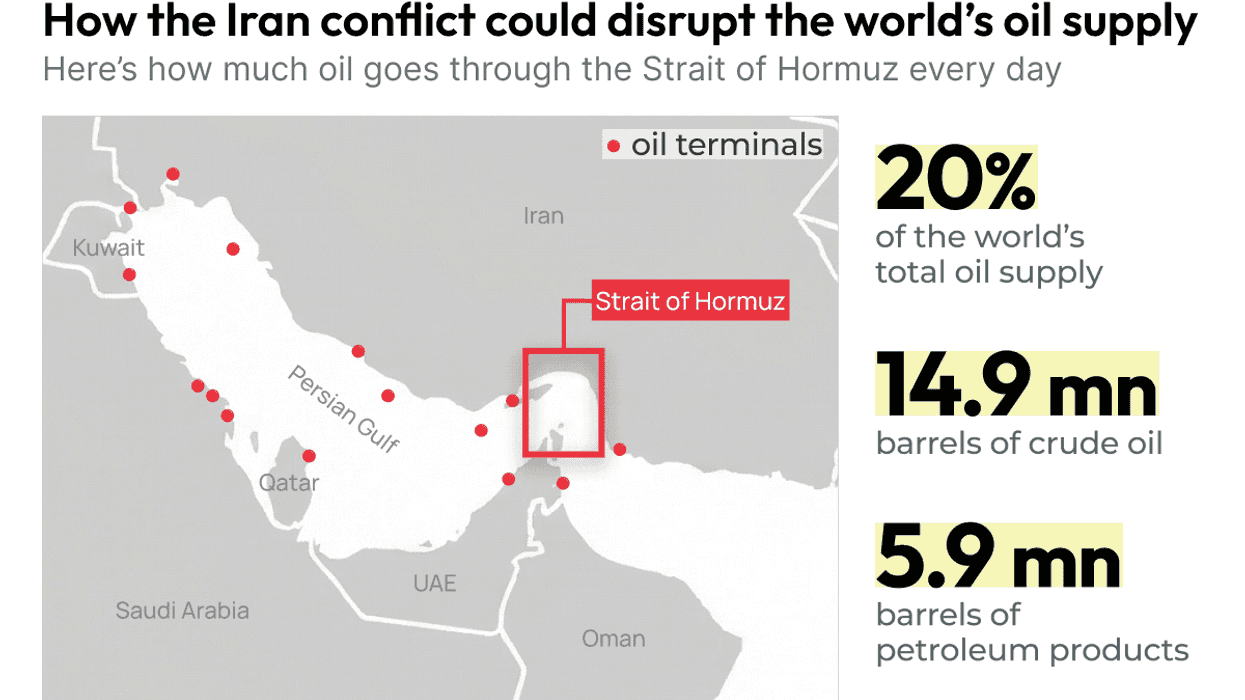
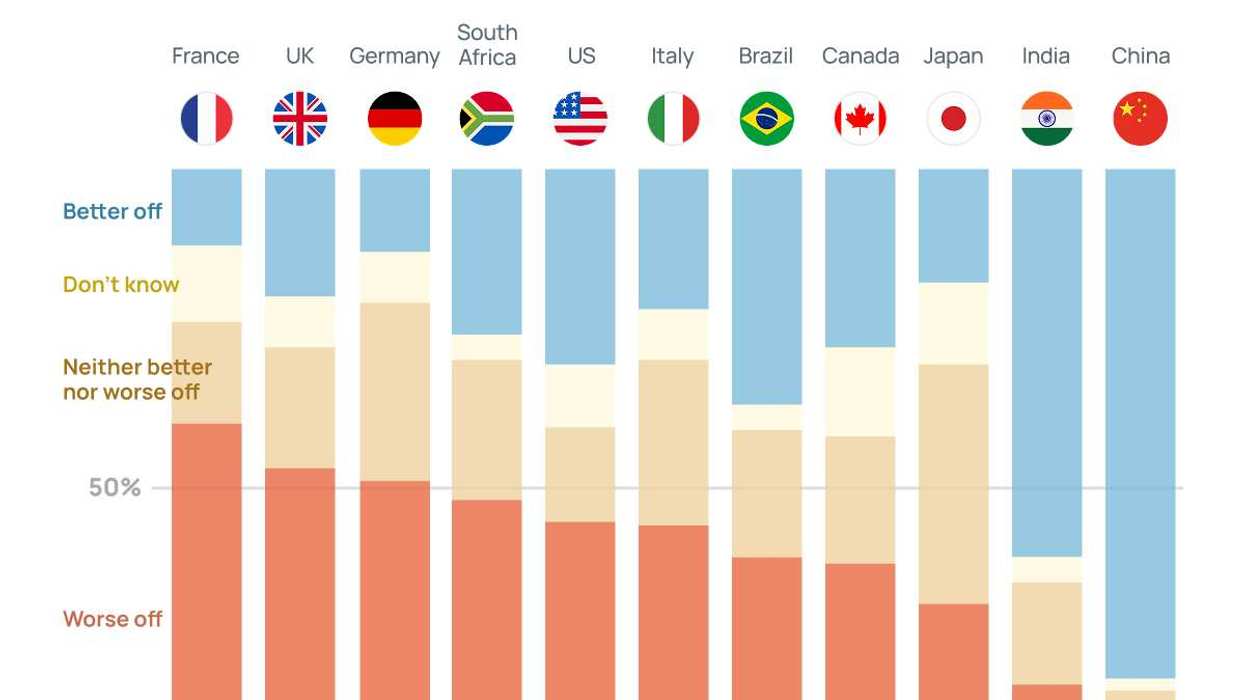
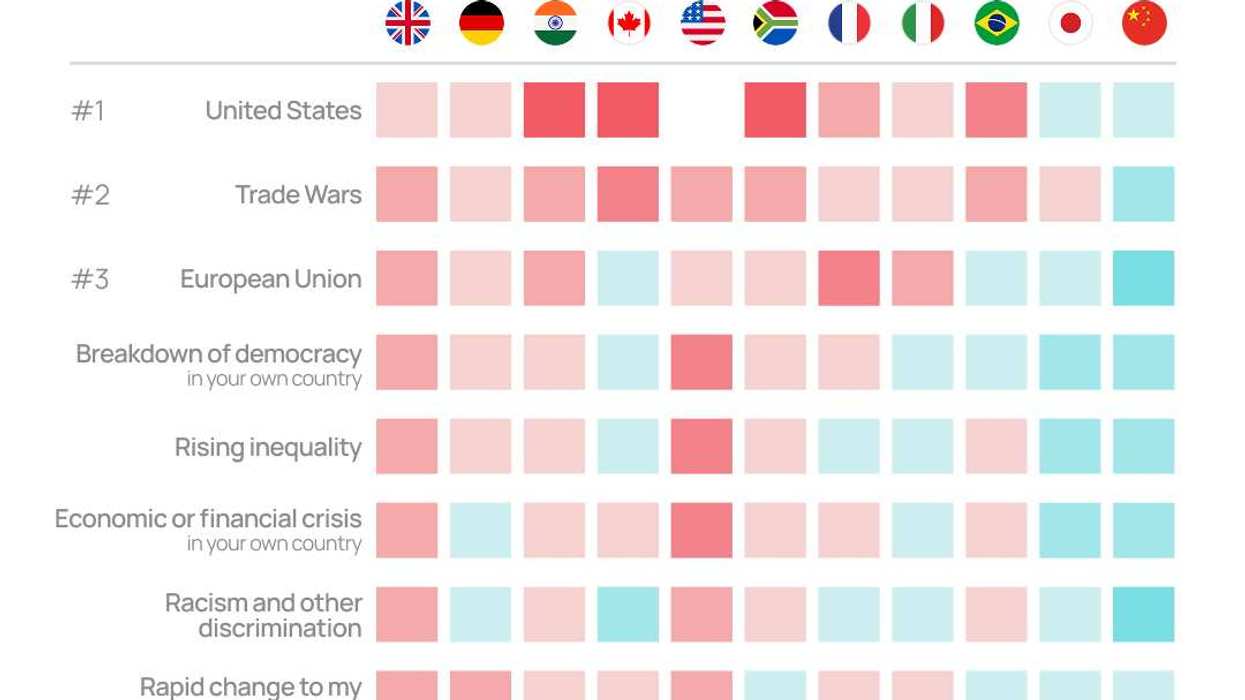
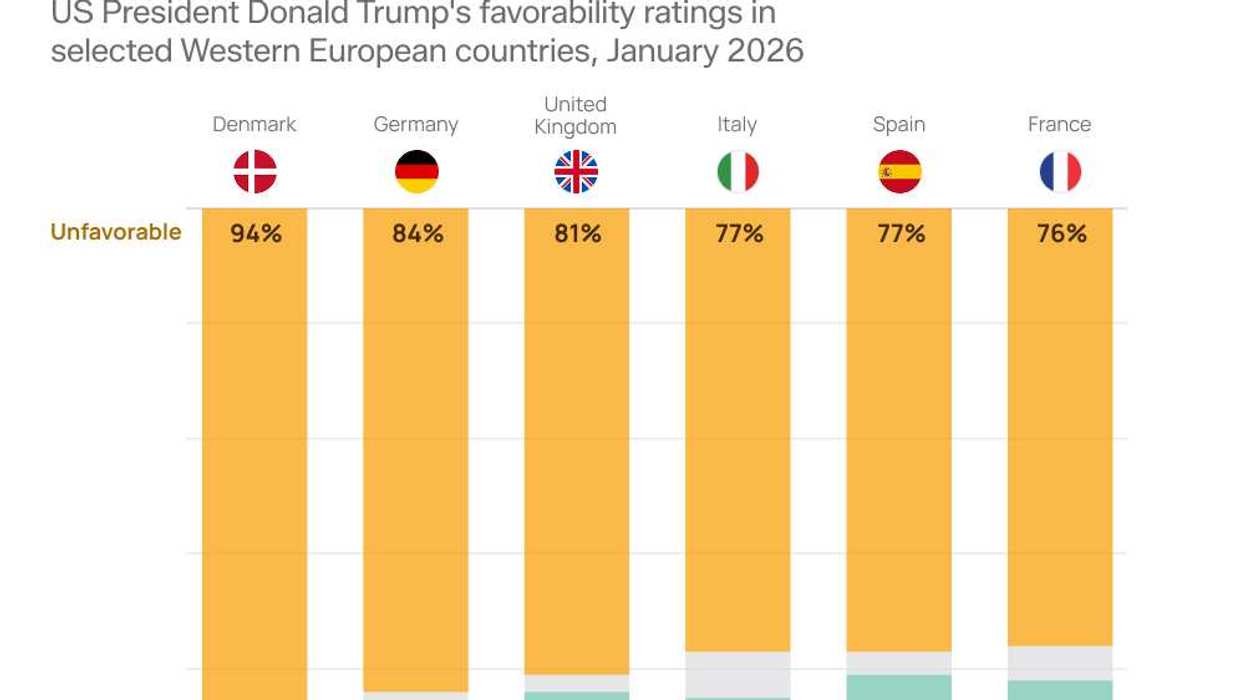
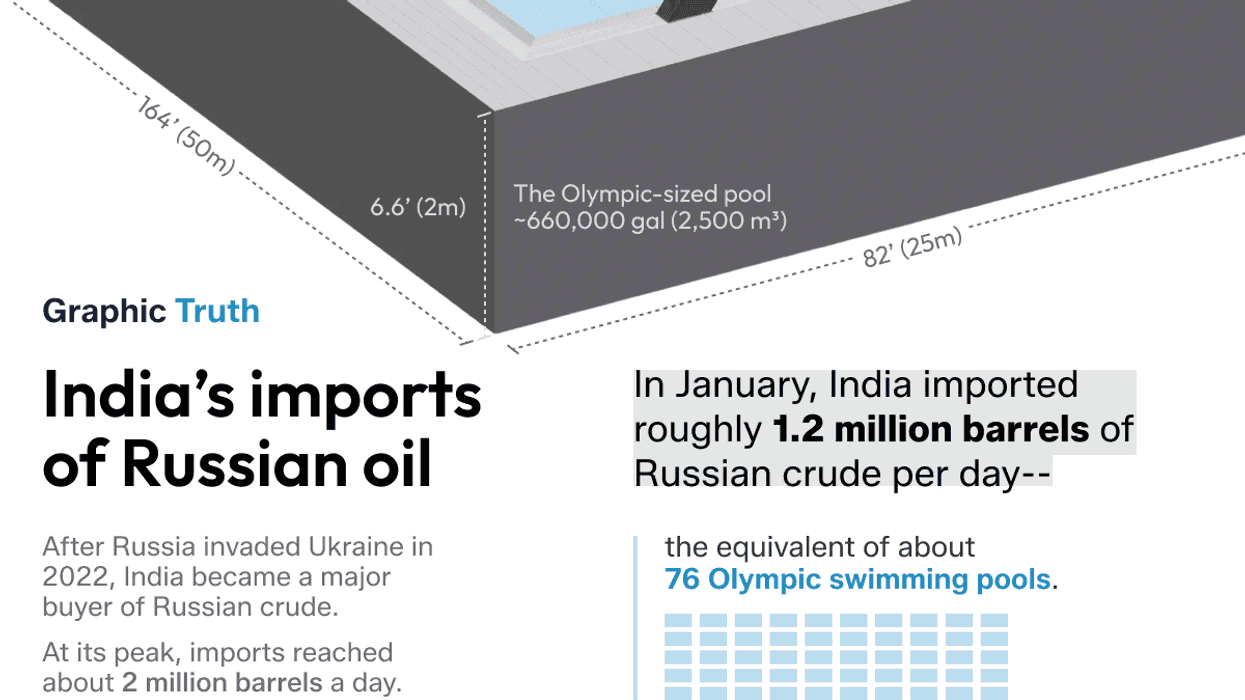
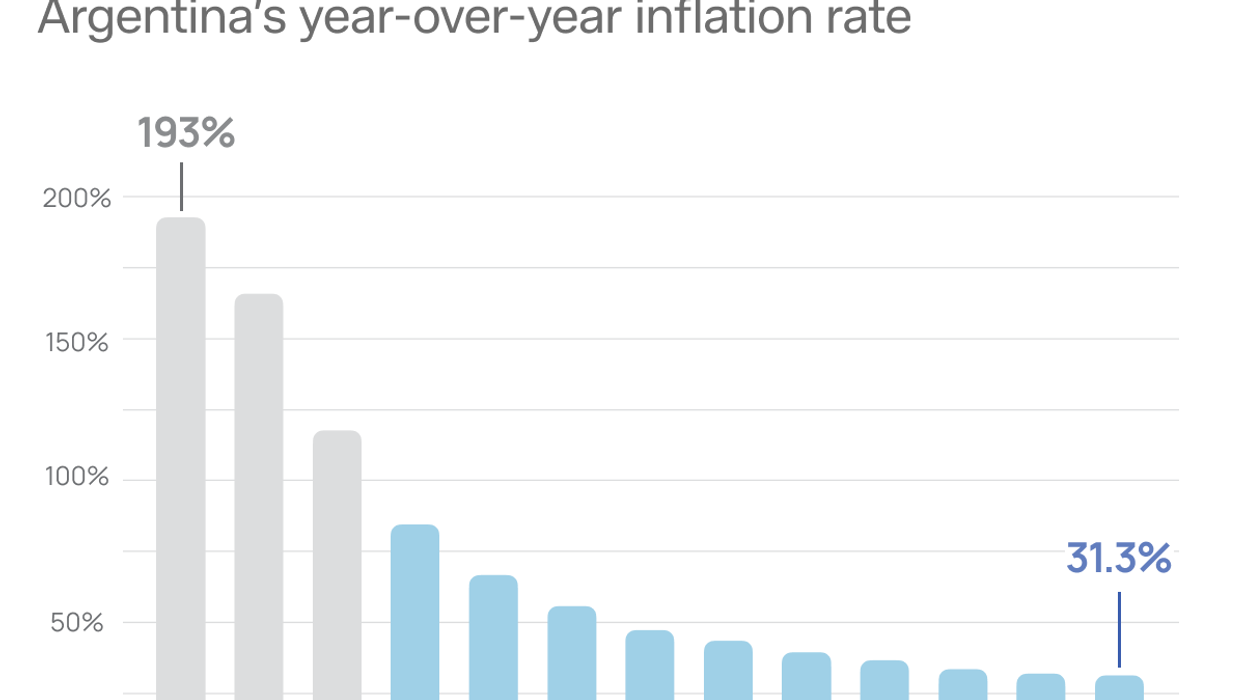
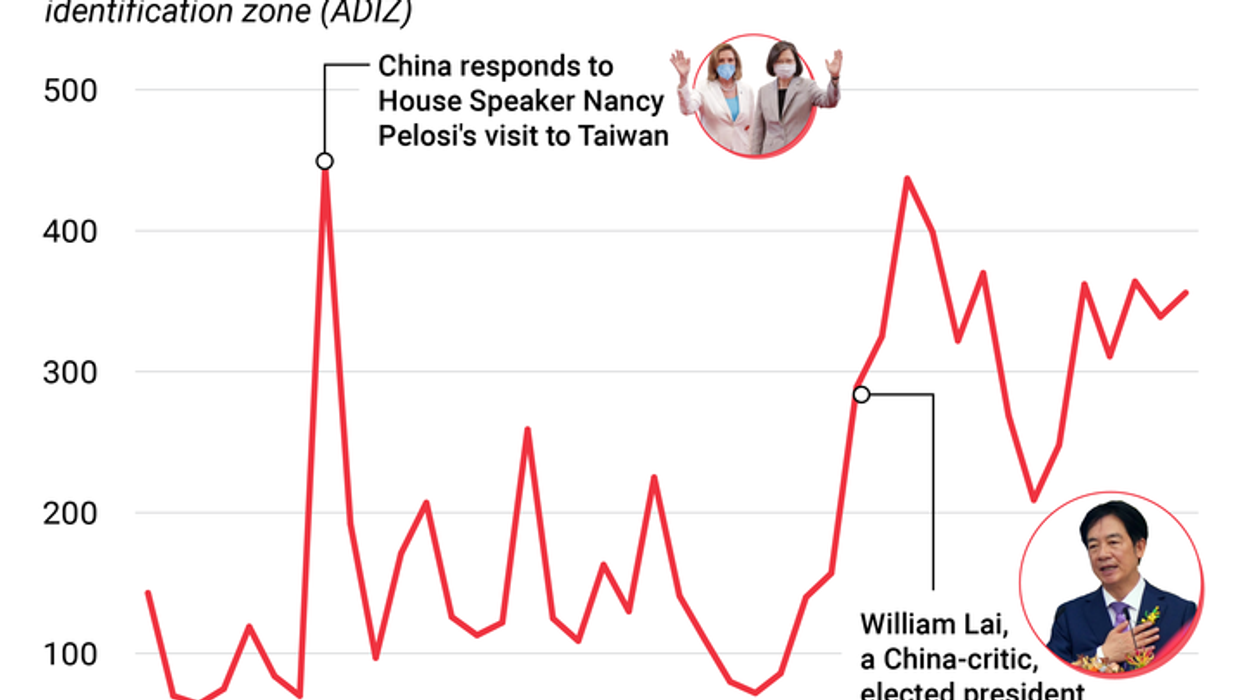
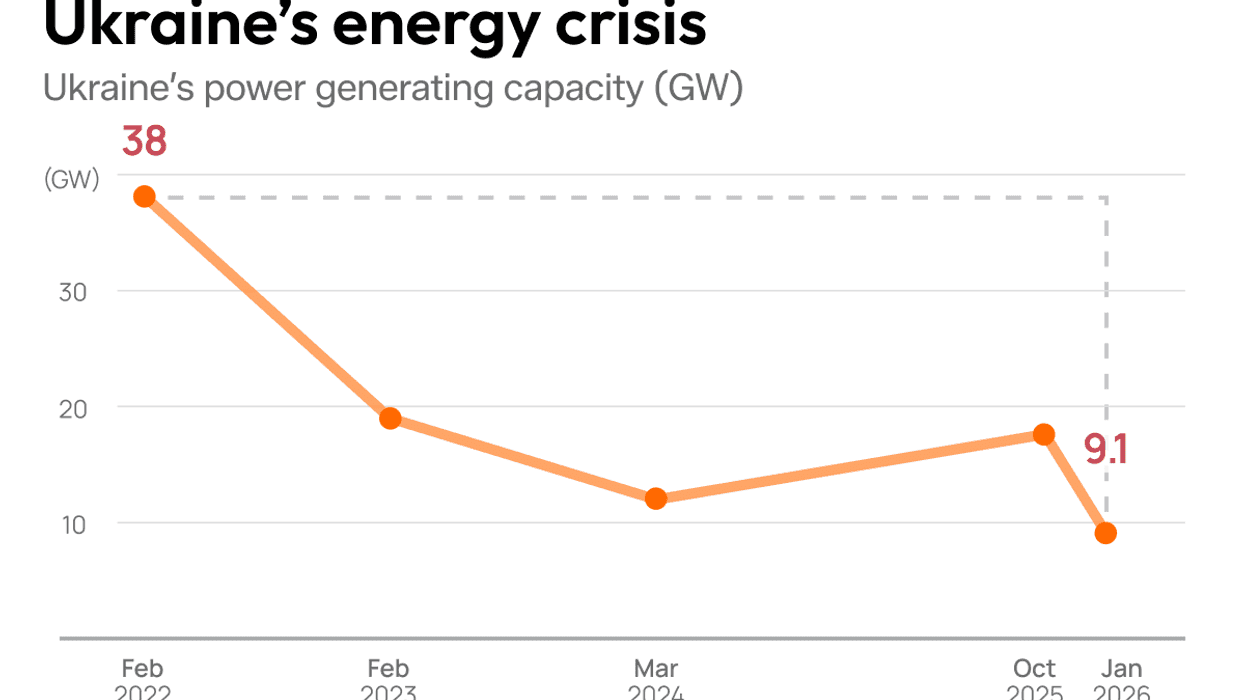Graphic Truth
Iran conflict: who could run out of weapons first?
The US and Israel have weapons and defense systems that are far more sophisticated than Iran’s. Precision missiles. Advanced radar. Missile defense systems stacked on top of each other.
Mar 04, 2026