What We're Watching
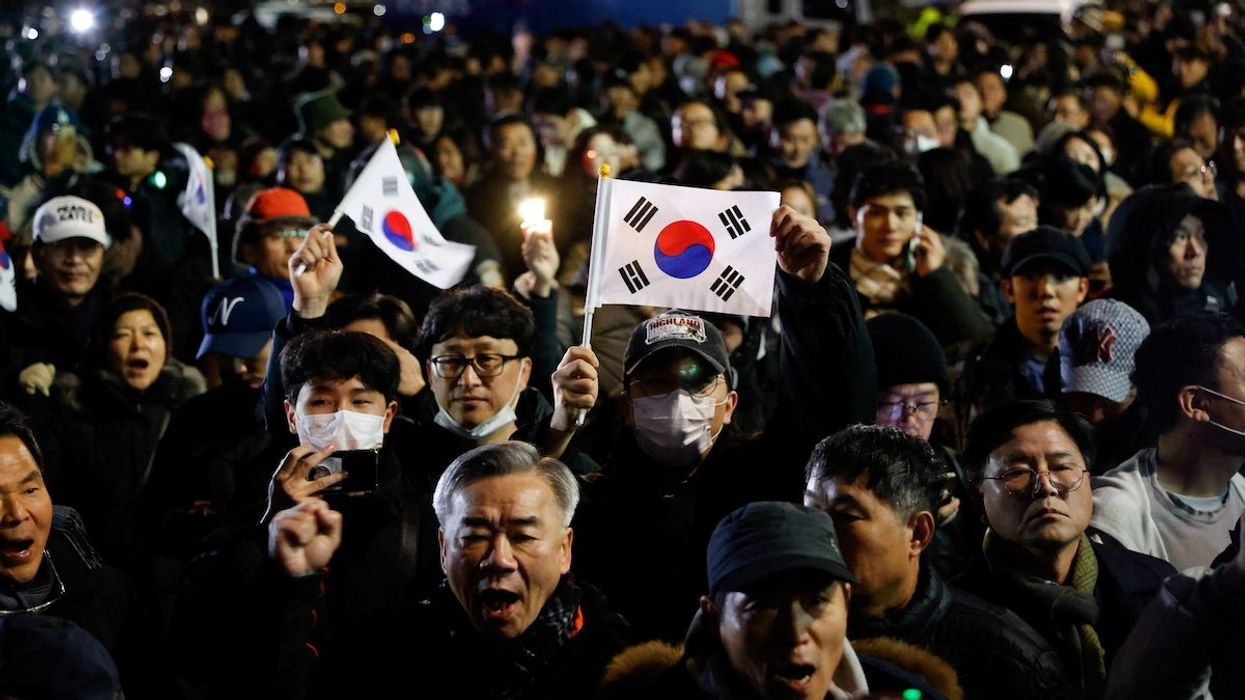
South Korean president ousted, election looms
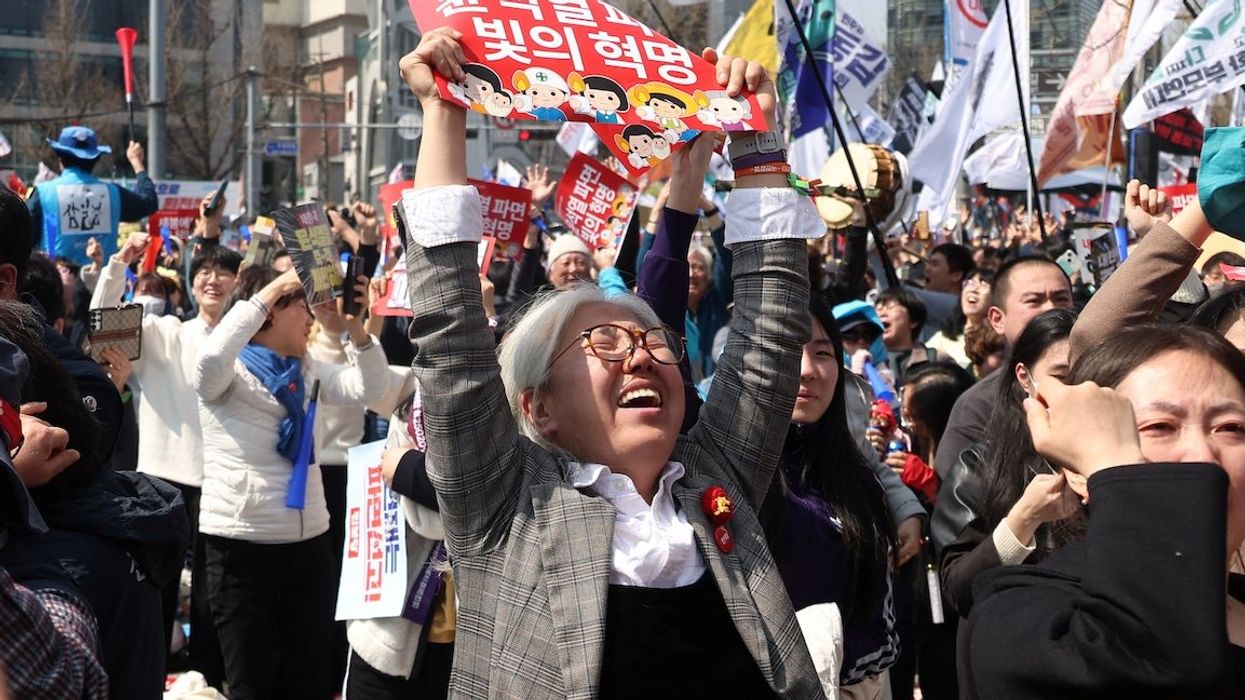
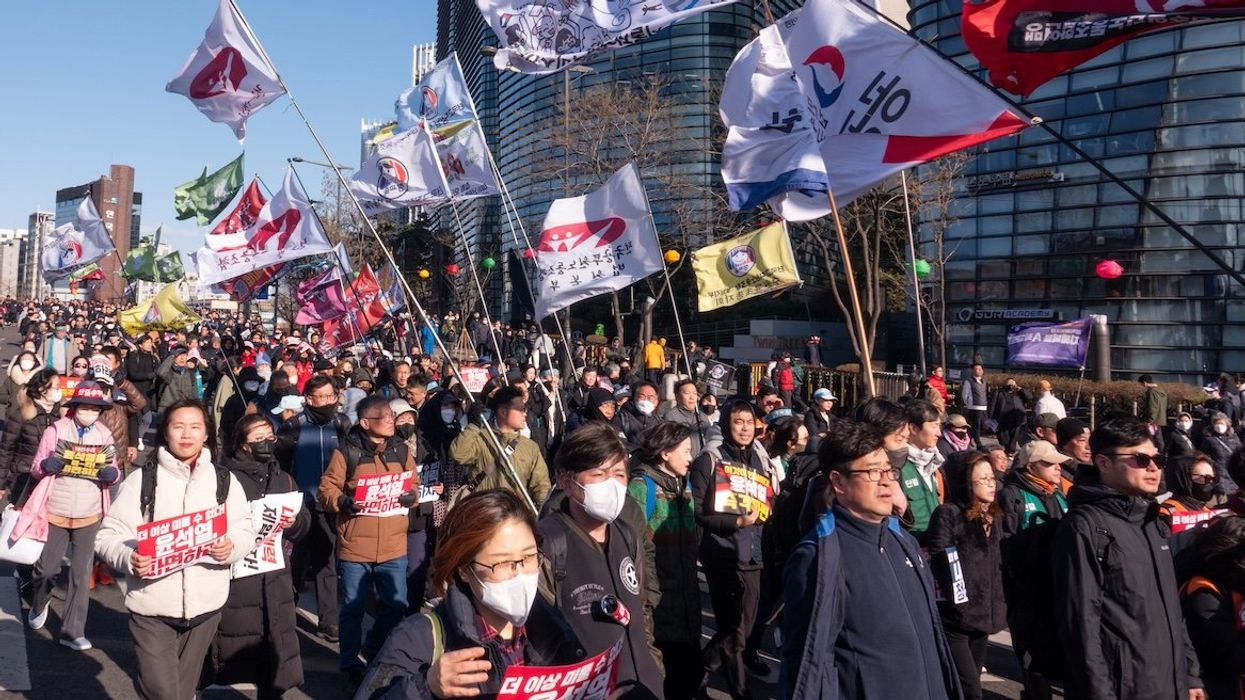
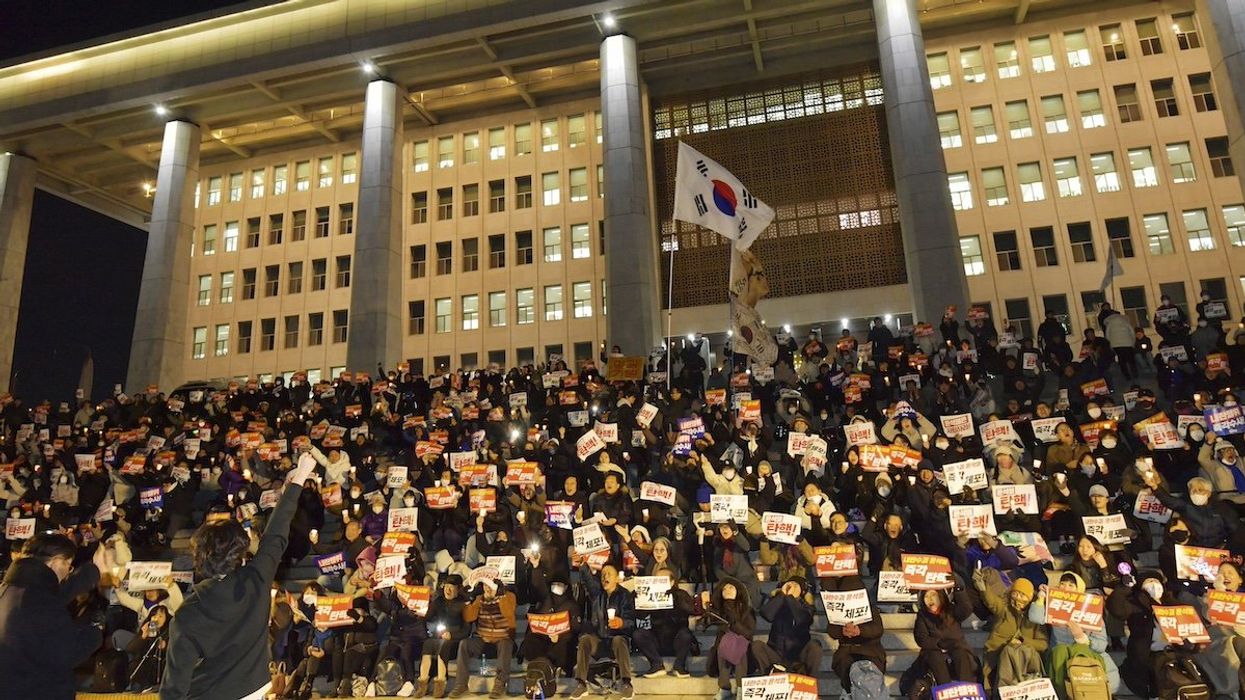
South Korea’s Constitutional Court on Friday voted unanimously to oust impeached President Yoon Suk-yeol over his decision to declare martial law in December. Supporters of Yoon who gathered near the presidential residence in Seoul reportedly cried out in disappointment as the court’s 8-0 decision was announced. Others cheered the ruling. The center-right leader is now the second South Korean president to be ousted.
Apr 04, 2025