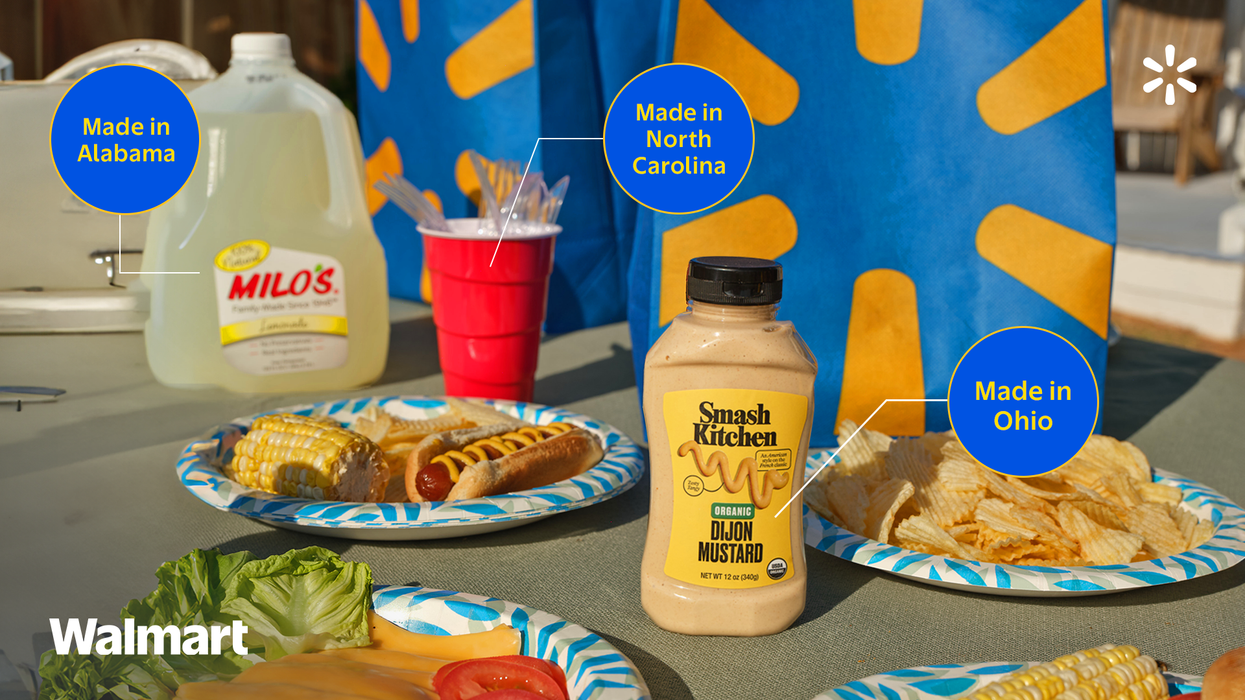
What We're Watching
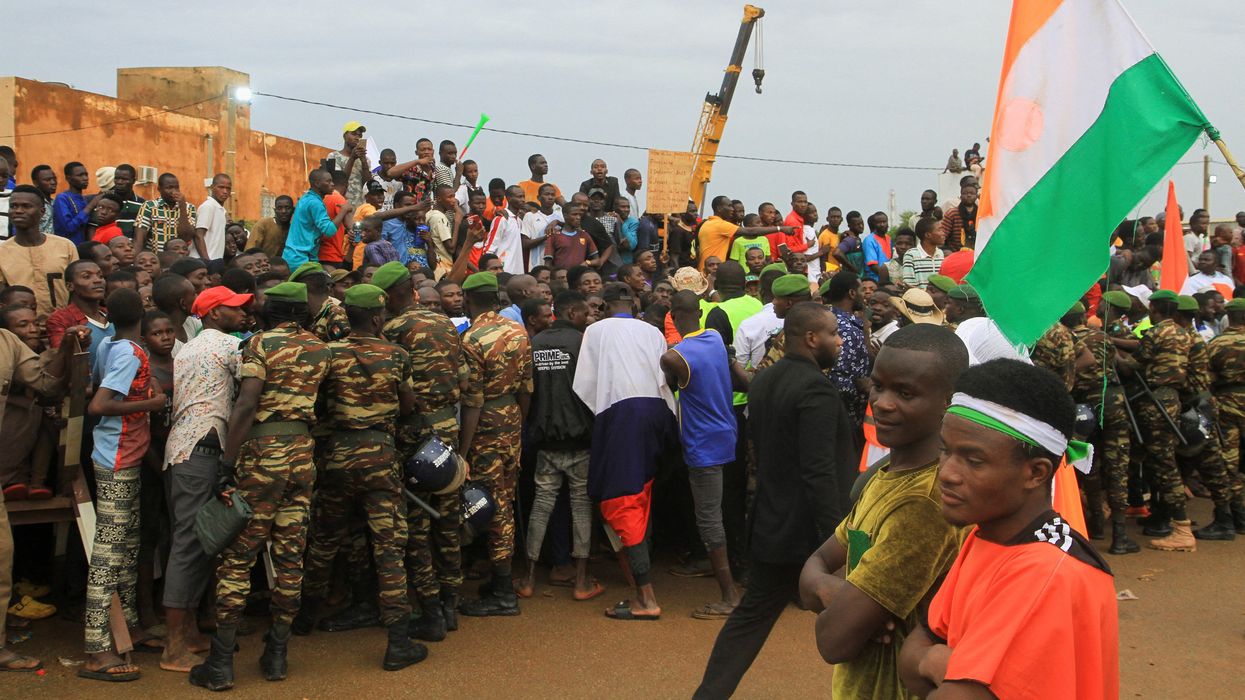
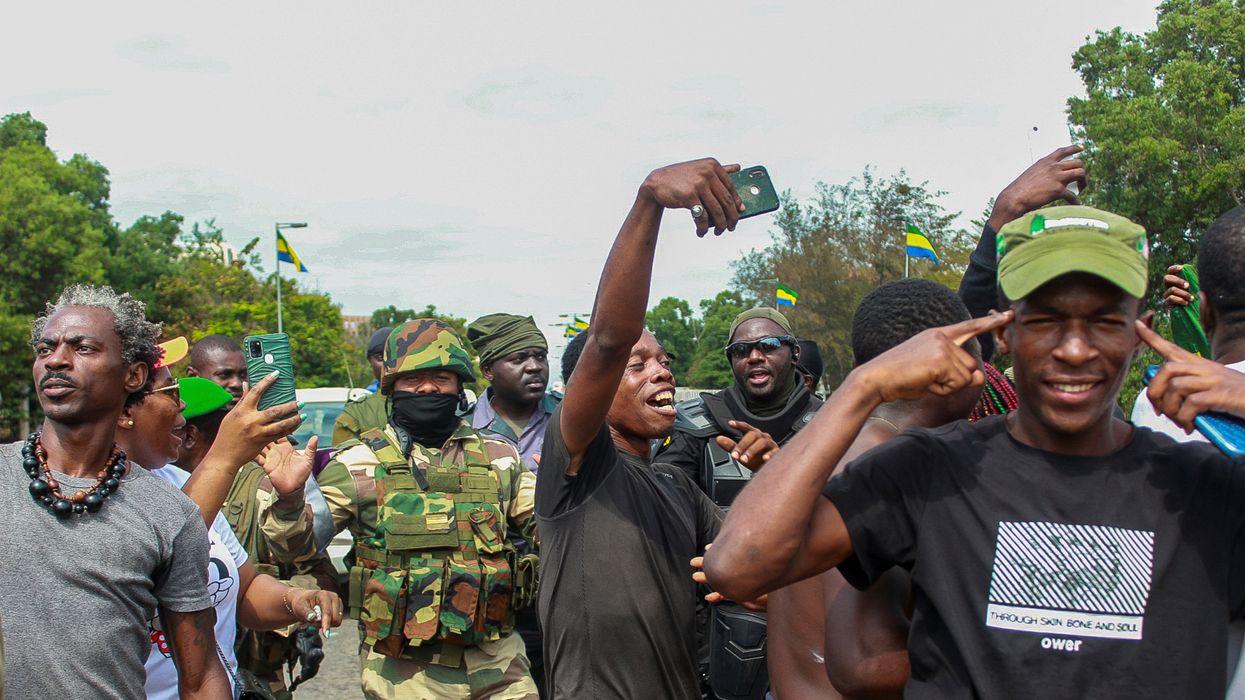
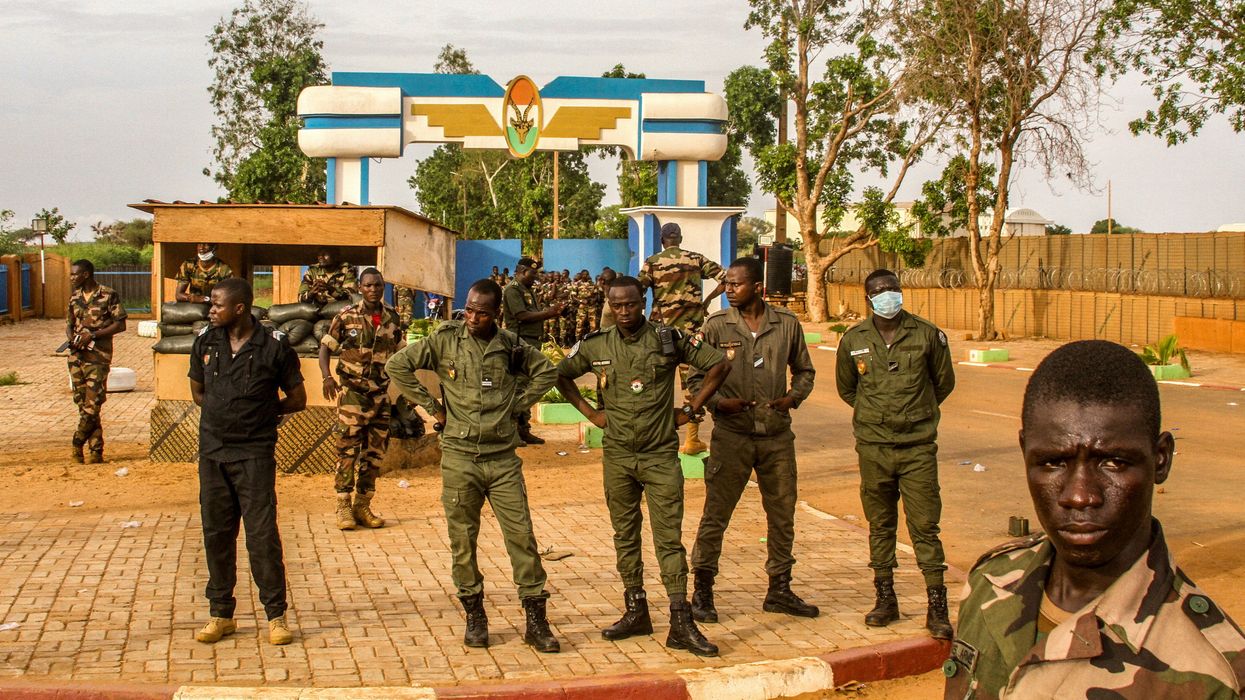
France to leave Niger
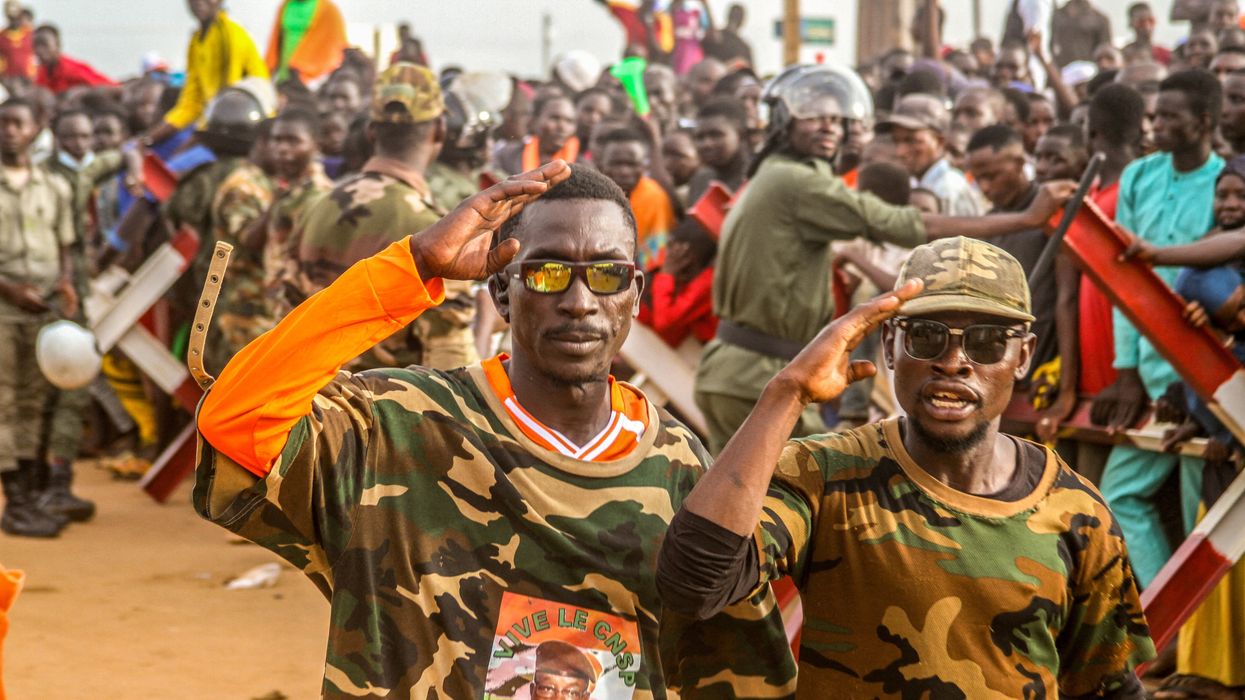
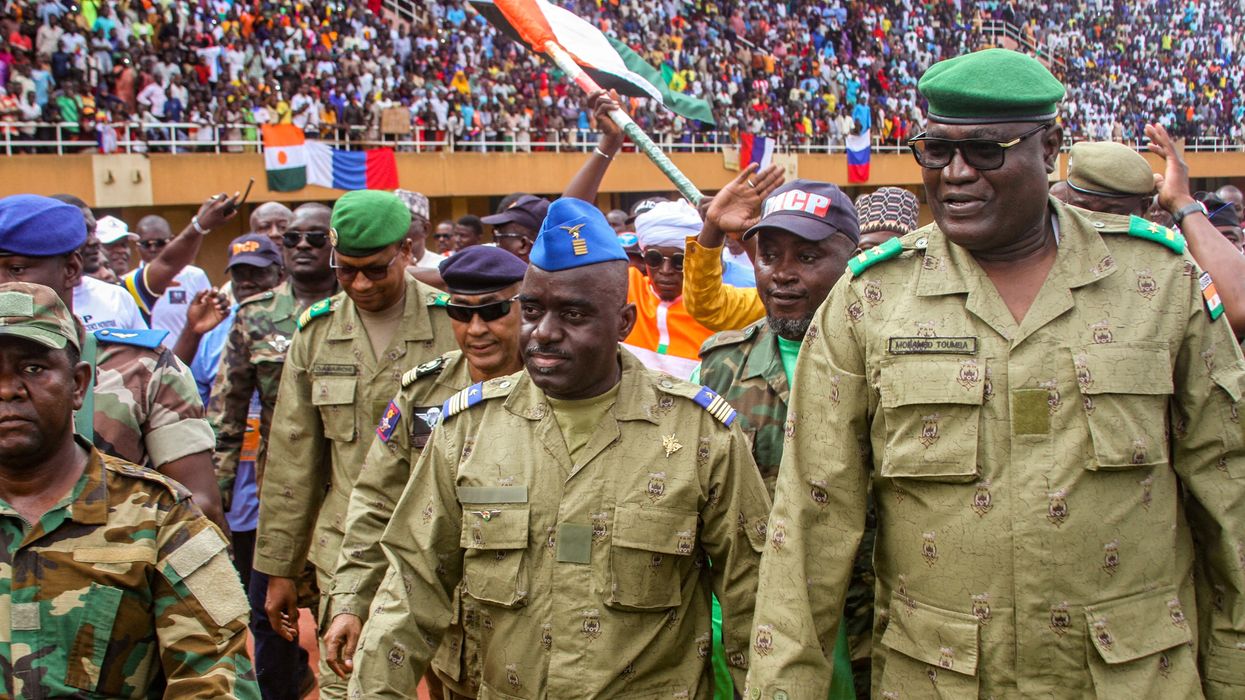
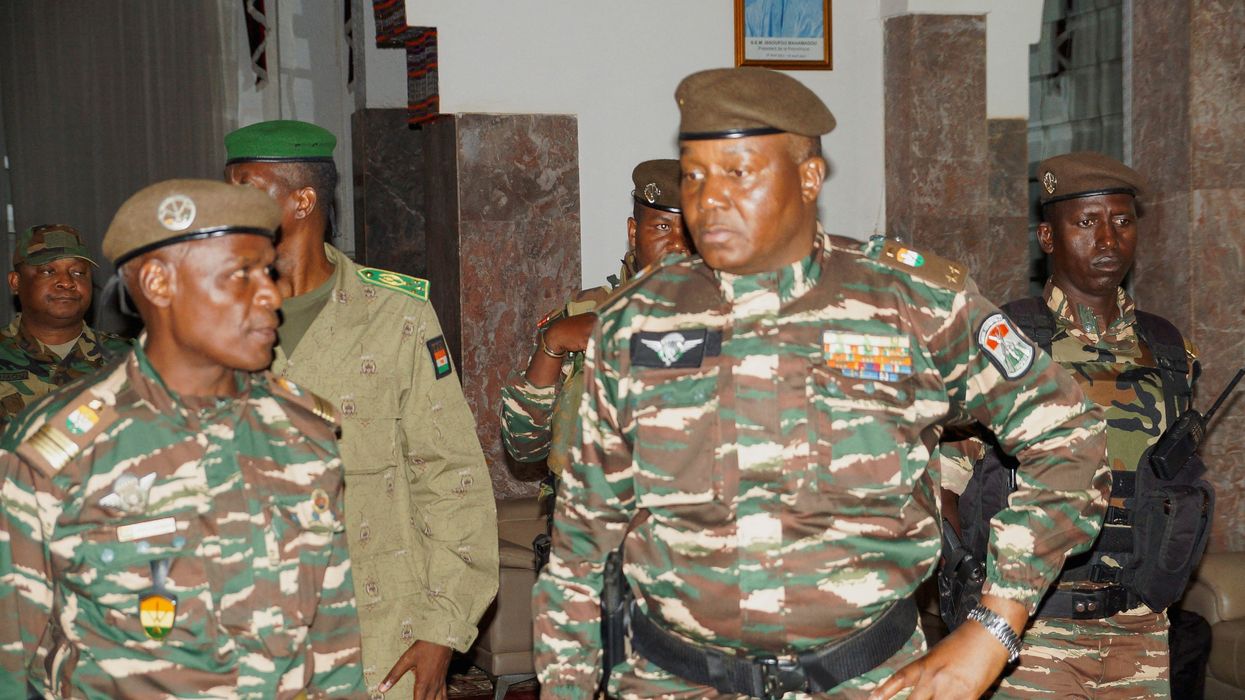
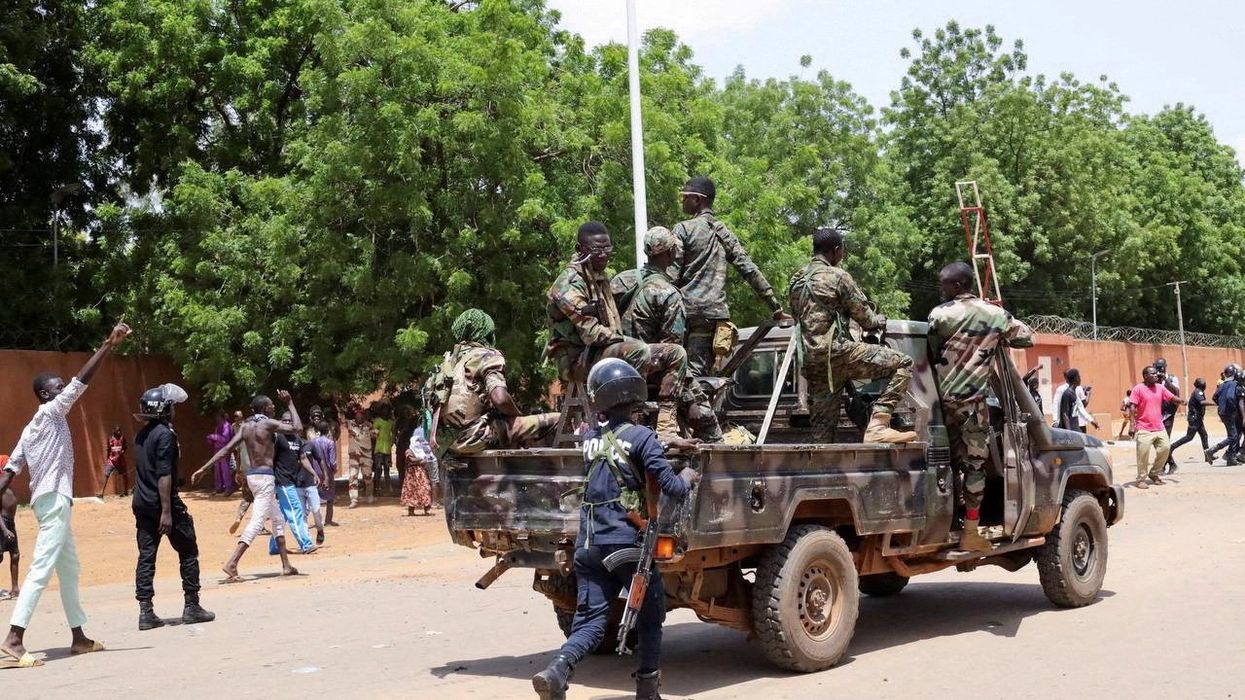
After a marked increase in anti-French sentiment following a military coup in Niger on July 26, French President Emmanuel Macron announced that France will immediately withdraw its ambassador and remove its 1,500 soldiers over the next few months.
Sep 24, 2023