News
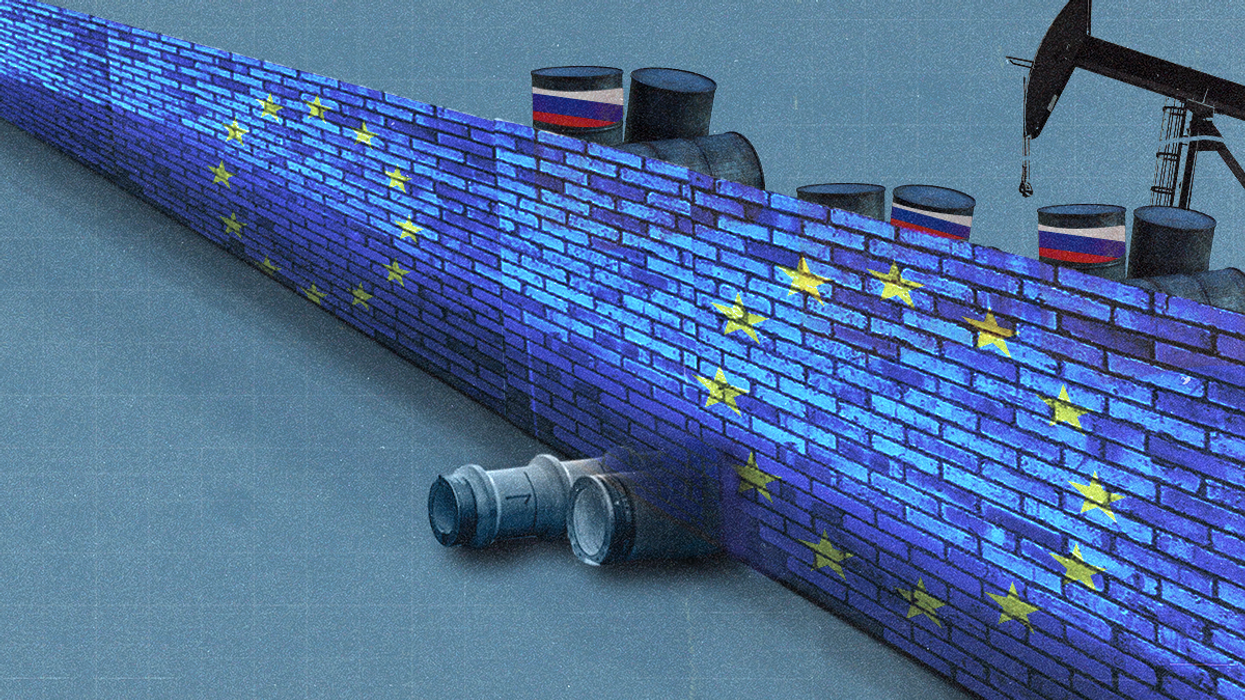
A guide to the EU’s lukewarm Russian oil embargo
After months of diplomatic wrangling, the European Union announced that it had reached an agreement to phase out Russian oil imports by the end of the year. But the agreement also includes a slate of carve-outs that could dilute the bloc’s effort to decapitate the Kremlin’s war machine.
May 31, 2022