Graphic Truth
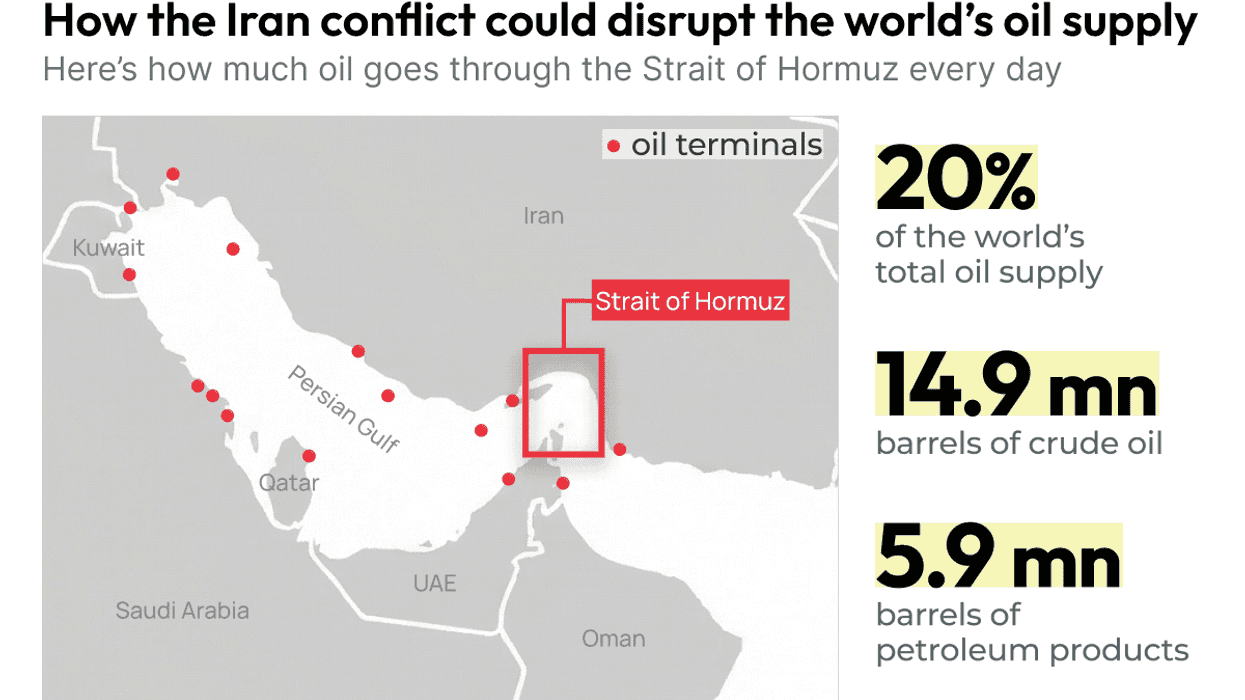
How the Iran conflict could disrupt the world’s oil supply
Shipping in the world’s most crucial oil chokepoint has nearly ground to a halt after at least four tankers were targeted in Iran’s retaliation to US and Israeli strikes on Saturday.
Mar 02, 2026