What We're Watching
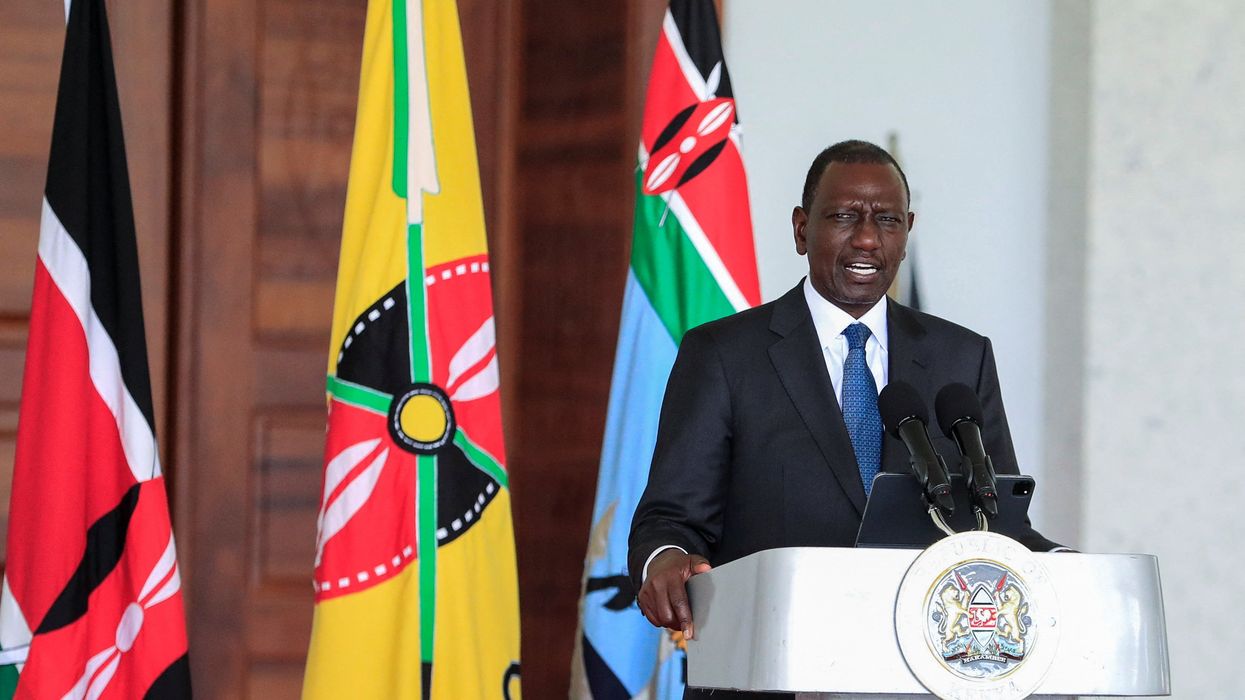
Kenyan president’s historic US visit: Haiti mission, trade, and China top agenda
This week, Kenyan President William Ruto is making a historic state visit to the United States, the first by a Kenyan leader in two decades.
May 21, 2024