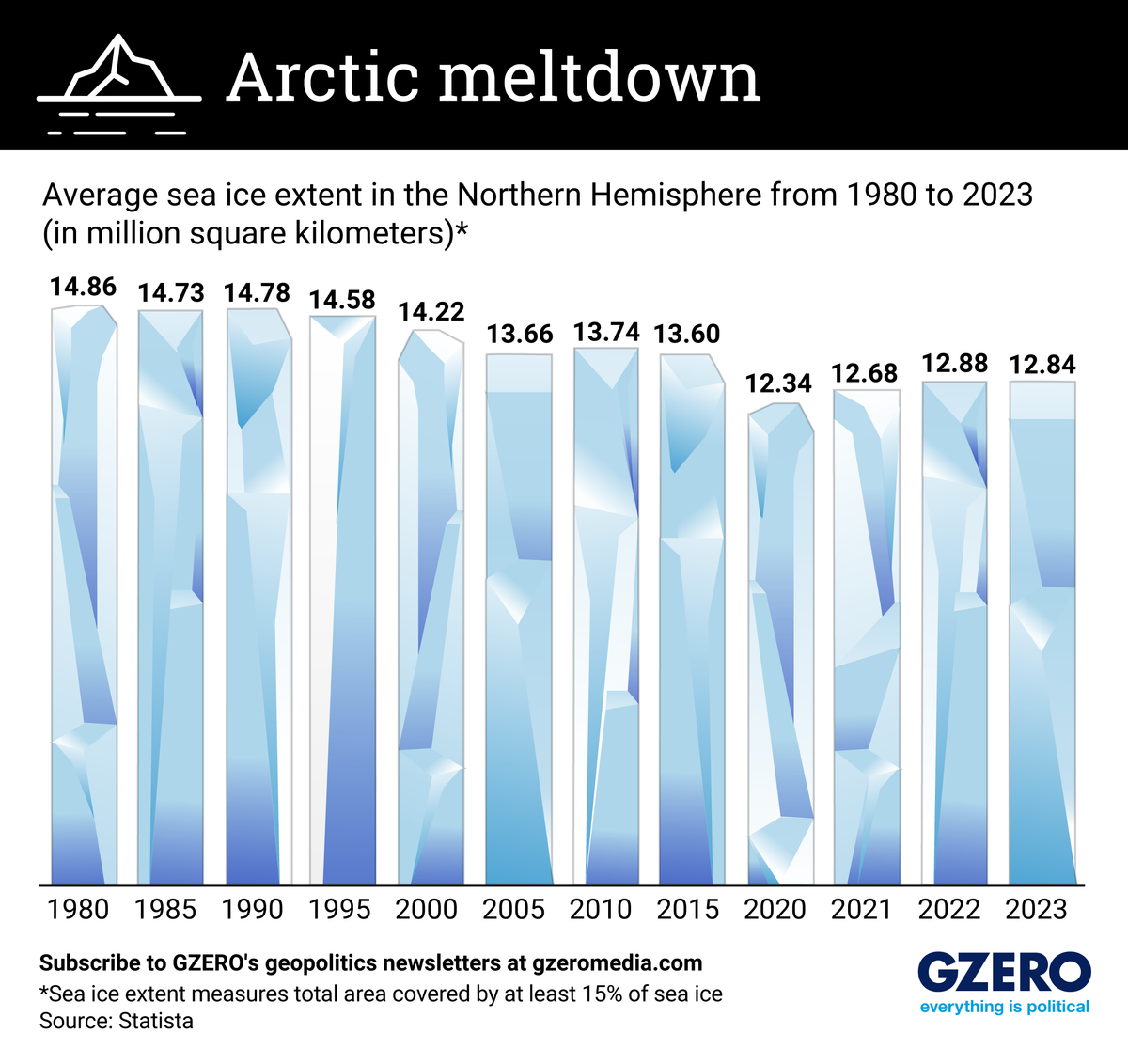
Ever since satellite observations started in the late 1970s, sea ice extent levels have been falling. That is the area of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice at any given time, which is important for the regulation of ocean and air temperatures, as well as safeguarding animal habitats.
But as the climate crisis deepens and sea temperatures rise, ice extent levels have reached historic lows. Meanwhile, as more ice melts, not only does it endanger wildlife, but it also fuels rising sea levels and releases methane into the environment that contributes to some of the worst climate catastrophes seen in recent years.
We take a look at sea ice extent levels from 1980-2023.