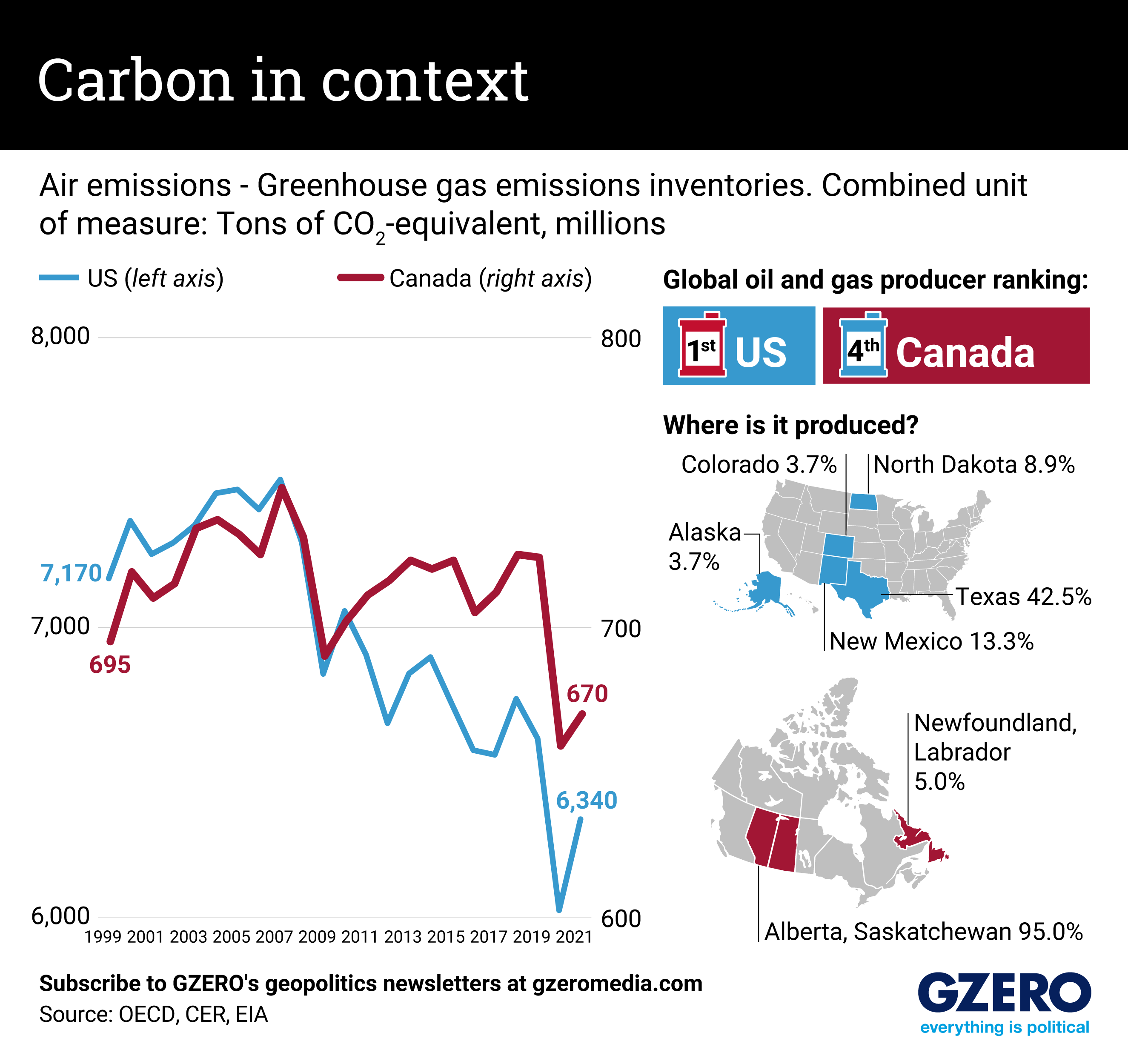
The US and Canada are both racing against the clock to lower their greenhouse gas emissions. As the effects of climate change become more apparent and deadly, countries are grappling with how to curb their emissions without curbing economic growth.
Canada, a resource-rich nation, is at a crossroads. Along with transportation and industry, the oil and gas sector dominates the country's emissions profile. Still, Canada has embarked on an ambitious journey to redefine its environmental legacy with one of the boldest climate commitments: pledging to reduce emissions by 40-45% below 2005 levels by 2030. Policies such as carbon pricing, identified as the top driver of emissions reductions, will prevent 226 megatonnes of carbon pollution from being released by 2030.
Meanwhile, the US energy sector, primarily powered by fossil fuels, is the largest source of emissions, contributing significantly to the nation's carbon footprint. Transportation, industry, and agriculture follow closely behind. But the US has made strides in addressing its emissions through a combination of federal mandates, state-level initiatives, and private-sector innovation. The Clean Power Plan and the Inflation Reduction Act, for example, are meant to incentivize the private sector to lead the way in renewable energy innovation and adoption.
Places where oil and gas are produced, however, may experience the most economic upheaval from the clean energy transition, while local communities near fossil fuel industries are more likely to experience environmental degradation and health impacts.