January 23, 2025
In the eight years since Donald Trump first arrived in the White House, US tariffs have risen considerably. During his first term, he imposed levies on tens of billions of dollars worth of goods from China and the EU to address perceived unfair practices by America’s main trade partners. (He also used tariffs to renegotiate the 1994 NAFTA free trade deal with Mexico and Canada, resulting in today’s USMCA.)
The Biden administration scaled back the EU tariffs but built on the China tariffs with additional measures. The tariffed share of US imports is now the highest it has been in decades, and Trump has threatened to boost tariffs even more.
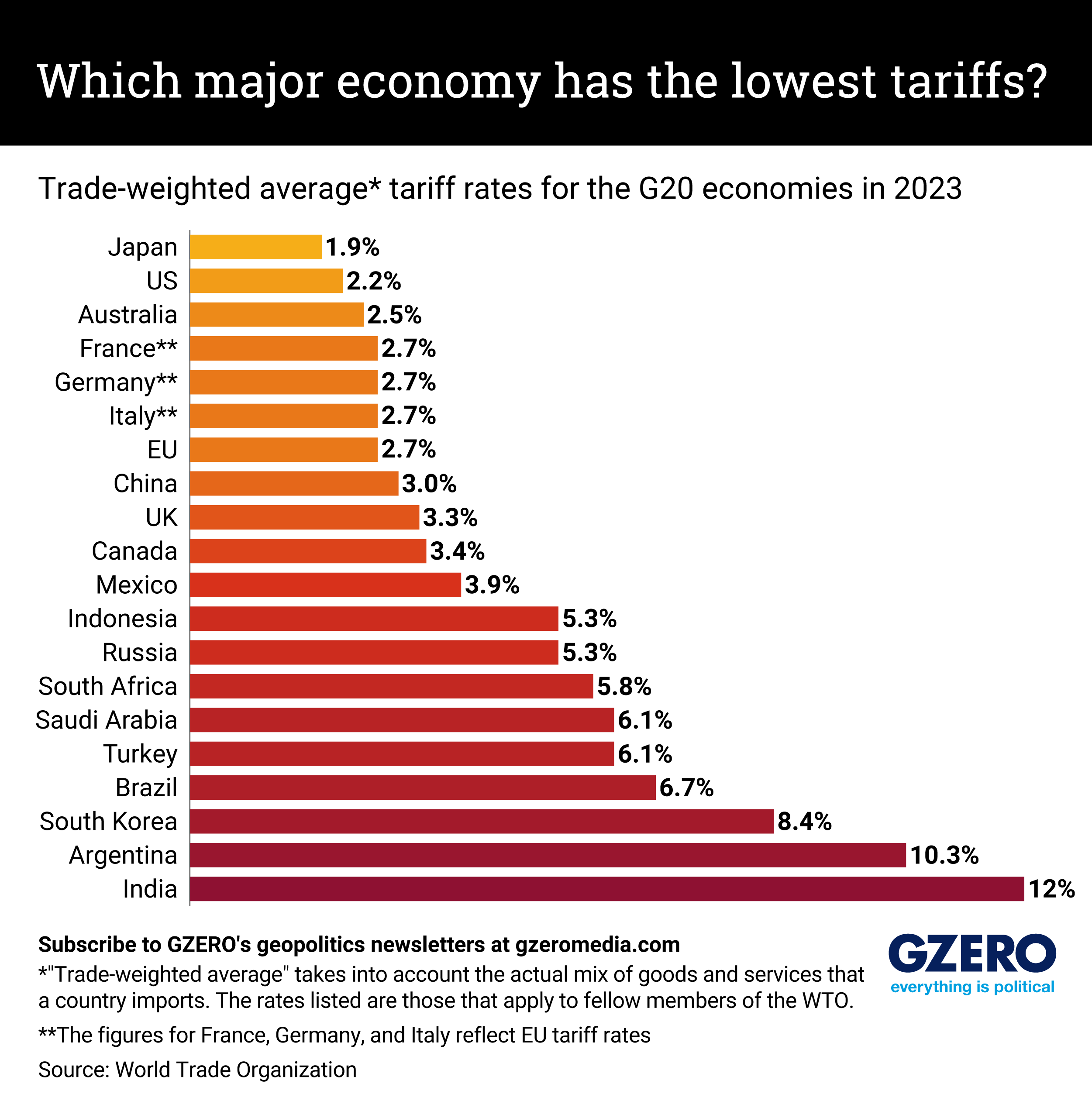
But he’s starting from what is still, despite all that, a low base. The US has the second-lowest tariff barriers among the G20, the group of the world’s largest economies.In 2023, the trade-weighted average US tariff rate – a measure that takes into account the mix of goods a country actually imports – was just 2.2%. Only Japan’s was lower. Canada’s, by comparison, was 3.4%. The EU’s was 2.7%. And India’s was a whopping 12%. Here’s a look at how all 20 economies stack up when it comes to levies at the border.More For You
Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskiy, Finland's President Alexander Stubb, Estonia’s Prime Minister, President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen and other European leaders visit memorial to fallen Ukrainian defenders at the Independent Square on the fourth anniversary of Russia's full-scale invasion, in Kyiv, Ukraine February 24, 2026.
Ukrainian Presidential Press Service/Handout via REUTERS
Somewhere in the Donbas region, Ukrainian soldier Artem Bondarenko says he hasn’t slept through the night in months as he defends Eastern Ukraine.
Most Popular
Members of the special units of the National Guard and the Secretaria de Seguridad Ciudadana stand guard in front of the Fiscalia General de la Republica, where the investigation into the operation in which Nemesio Oseguera Cervantes, alias "El Mencho", founder and leading head of the Cartel de Jalisco Nueva, was killed, is underway.
Félix Márquez/dpa via Reuters Connect
- YouTube
In this Quick Take, Ian Bremmer warns that US military strikes on Iran are “looking increasingly imminent” as diplomacy appears to stall.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.