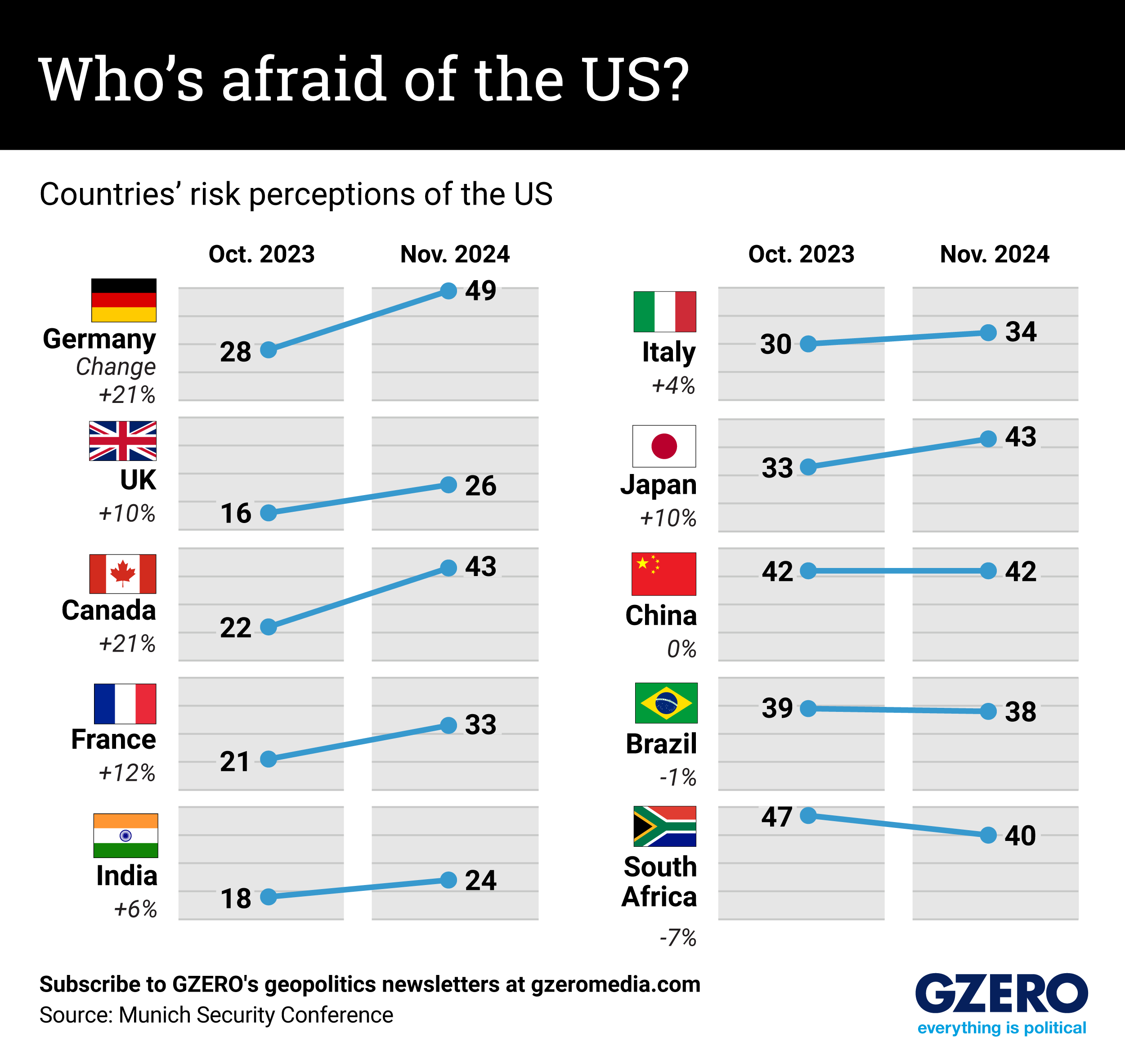
Each year, the Munich Security Conference – the Super Bowl of international security events – asks leaders what they believe are the biggest risks facing their countries. This year’s poll found that fears of the US skyrocketed in seven of the 10 countries surveyed between October 2023 and November 2024, as Donald Trump’s return to the White House went from possibility to reality.
Risks perceptions of the US increased the most for Germany and Canada – growing by 21 points each. For Germany, the jump was likely fueled by memories of Trump’s first term, when he cast doubt on NATO and threatened to withdraw troops from Germany, combined with campaign trail threats to halt Ukraine aid and implement tariffs on the EU. Canada, meanwhile, knew it would soon face the threat of 25% tariffs from its biggest trading partner. Notably, this data was taken before Trump began threatening to make Canada the “51st state,” and could be higher today.
The only country where risk outlooks stayed the same was the US’ greatest rival, China. It decreased by 1 point in Brazil, and by 7 points in South Africa – where the government likely did not foresee Trump’s ally, Elon Musk, taking issue with its recent land policy and Trump threatening to halt aid to the country.
“The United States today is the biggest driver of geopolitical uncertainty on the global stage,” says Eurasia Group and GZERO founder Ian Bremmer. “Uniquely in modern history, it’s a country committed to unwinding large pieces of a global order that the United States itself has built and led.”