In the coming decades, Arctic sea ice is expected to melt so much that the region will become traversable much of the year. While environmentally devastating, this will also mean more shipping access, resource extraction, and risk of conflict in the region.
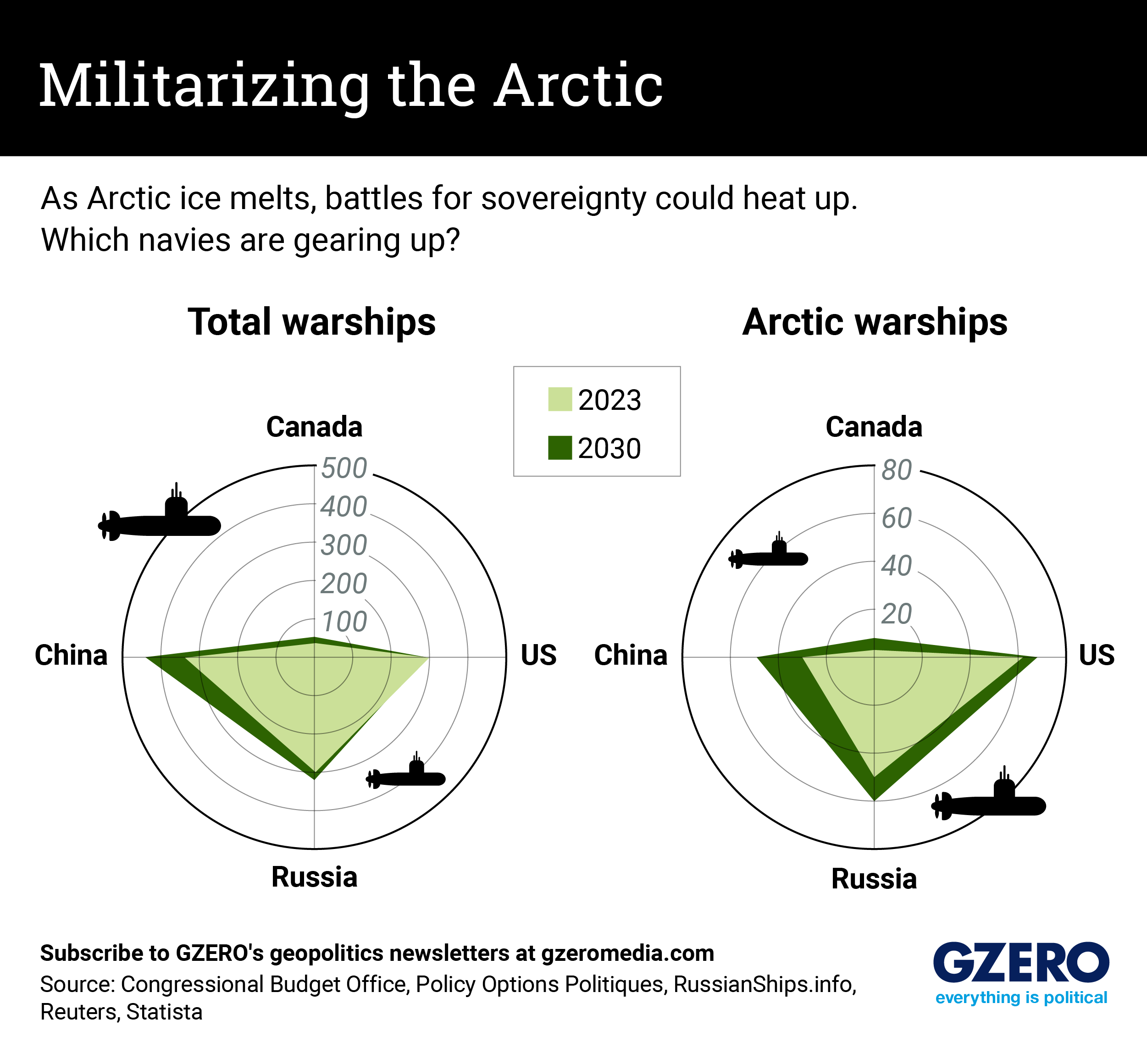
Any future battles for sovereignty in the Arctic will rely on access to icebreakers and submarines. Canada has been trying with little success to grow its navy since it enacted its National Shipbuilding Strategy in 2010, and its plan to open an Arctic naval facility is nearly a decade behind schedule. The US, meanwhile, has a formidable submarine fleet, but its naval interests are spread worldwide, and Washington has not indicated any plans to make the Arctic a priority anytime soon. This means the US and Canada will need their NATO partners and allies to help keep an eye on security threats up north.
Arctic naval dominance, meanwhile, is shifting eastward. China looks set to outpace all other countries in naval growth through 2030. It is also joining major Arctic institutions, sending high-ranking officials to the region, and using its naval vessels to patrol Arctic waters – all signs that China has great polar power ambitions.
The strategic importance of the Arctic has also been on Russia’s radar. Over the past decade, Moscow has invested in around 40 icebreakers, giving them a mammoth fleet compared to other nations. While the US and NATO’s submarine fleets are expected to constrict in 2030, Russia is planning to grow its submarine capacity.
We take a look at Arctic-capable warships across these four countries.