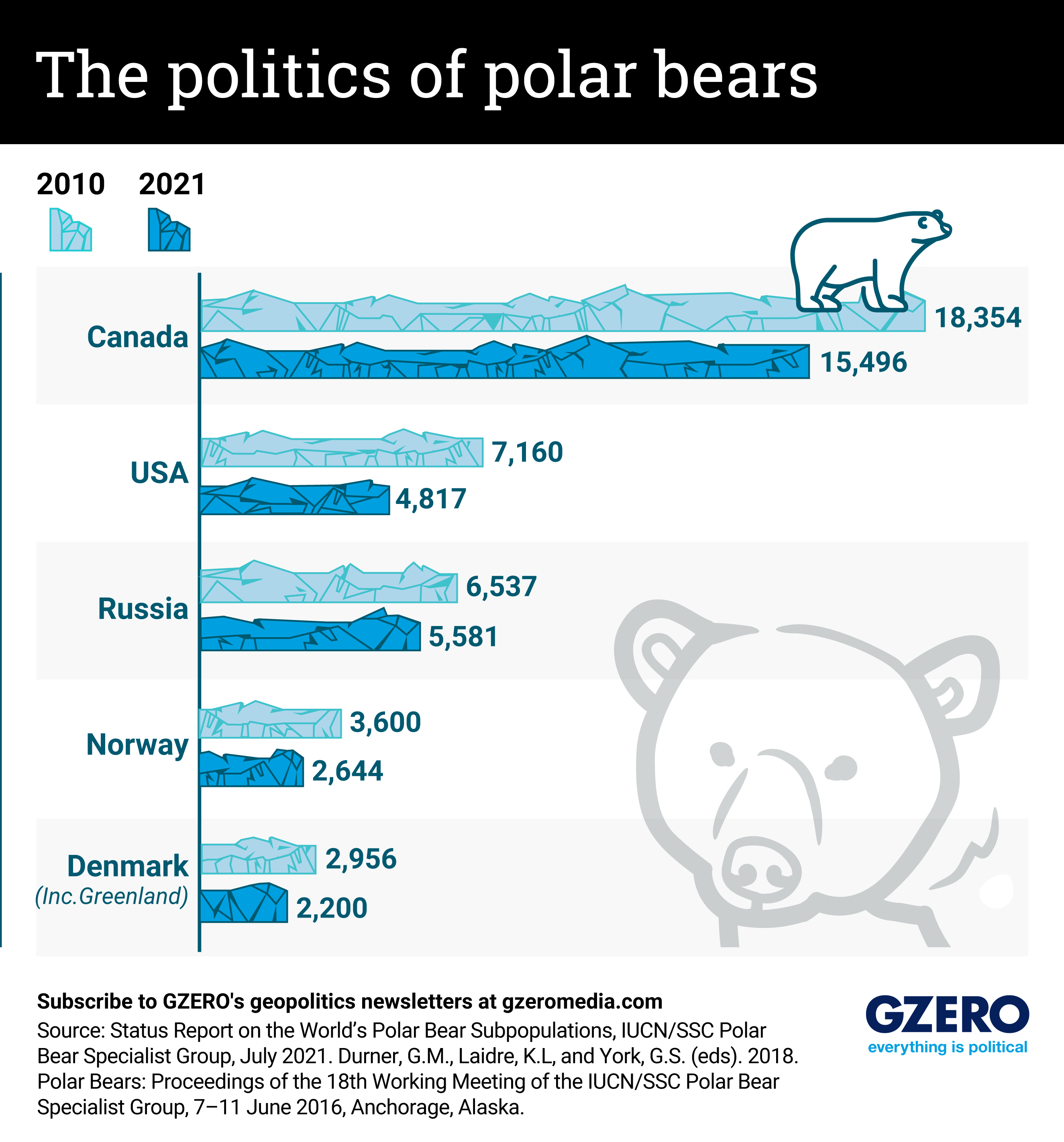
There’s a new “cold” war playing out through inaction on climate change, and it’s melting ice in the Arctic. The casualties? Polar bears. Nanuit – as they’re called in Inuktitut (the language of the Inuit) – roam across the Arctic, and can be found in the US, Canada, Russia, Greenland, and Norway. They rely on sea ice to hunt, mate, and raise their young, making them particularly vulnerable to climate change.
The Arctic is warming two times faster than the rest of the world because of climate change. A new UN report says the world is likely to breach the 1.5-degree Celsius climate threshold by 2027 due to El Niño and human-caused climate change. While the initial breach would only be temporary, scientists are 98% certain we will permanently breach it within a decade unless industrialized nations join together to slash greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030.
Two-thirds of the world’s polar bears could be gone by 2050 if the Arctic keeps warming at its current speed. As of 2023, there are an estimated 22,000 to 31,000 polar bears left in the world. Long-term figures on polar bear populations in the northernmost regions are lacking, but data shows an undeniable downward decline over just the past decade. We look at how polar bear populations have changed across the five countries they call home (with the caveat that polar bears don’t respect borders).