December 02, 2022
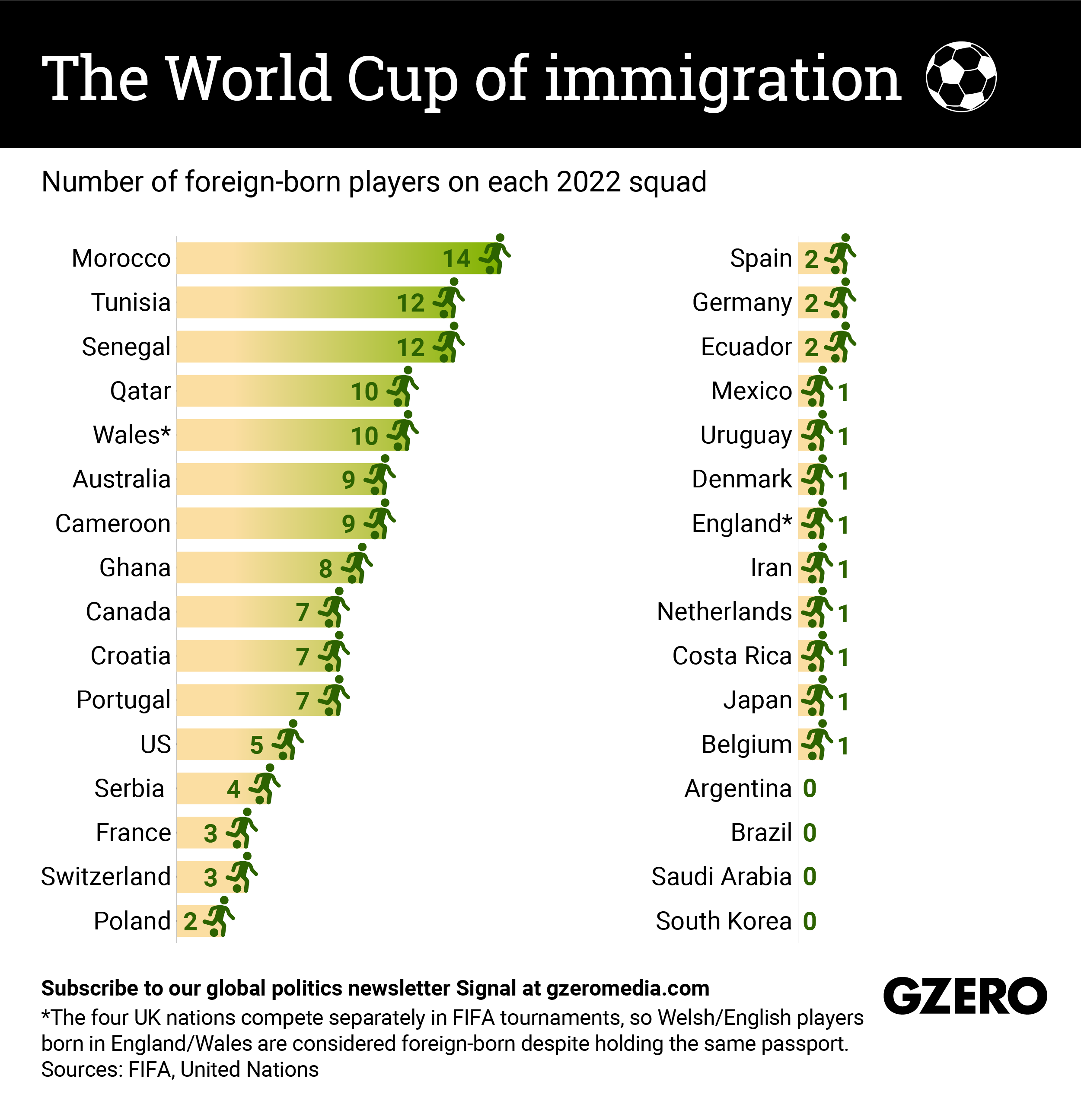
If you're a soccer player, your dream is to compete in the World Cup — with whatever country will call you up, whether you were born there or not. About 10% of players in the 2022 edition of the tournament in Qatar are foreign-born.
But this is nothing new. Almost 14% of players in Italy '90 were foreign-born and in the colonial era legends like striker Eusébio from Mozambique defended the colors of Portugal. What's more, when FIFA's eligibility standards were more lax, players were allowed to switch sides. José Altafini won the trophy with his native Brazil in 1958 and four years later didn’t repeat victory because he’d signed up for Italy, his adopted country. Wars matter, too: Robert Prosinecki played for Yugoslavia in 1990 and later for independent Croatia in 1998.
Also, the distribution of foreign-born players in Qatar 2022 is unequal: While half of Morocco's squad was not born in Morocco, four teams — Argentina, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea — have no foreign-born players at all. Fun fact: The Williams brothers, both born in Spain, are playing for different countries — the older Iñaki is realizing his grandfather's dream by playing for Ghana, where the family's roots are, while Nico is with La Roja.
We take a look at the number of foreign-born players in World Cup national squads.
More For You
Chris, an Army veteran, started his Walmart journey over 25 years ago as an hourly associate. Today, he manages a Distribution Center and serves as a mentor, helping others navigate their own paths to success. At Walmart, associates have the opportunity to take advantage of the pathways, perks, and pay that come with the job — with or without a college degree. In fact, more than 75% of Walmart management started as hourly associates. Learn more about how over 130,000 associates were promoted into roles of greater responsibility and higher pay in FY25.
Most Popular
- YouTube
In this Quick Take, Ian Bremmer examines the second week of the US-Israel war with Iran and warns that the conflict risks spiraling into a longer and more destabilizing situation.
Center-right Colombian Sen. Paloma Valencia will head into May’s presidential election with some momentum, after 83% of voters opted to vote in the right-wing primary on Sunday – which she won comfortably.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.