How do civilians prepare for a war they aren't sure is coming? With a possible Russian invasion looming, we got some views on what life is like on the ground in several cities across Ukraine.
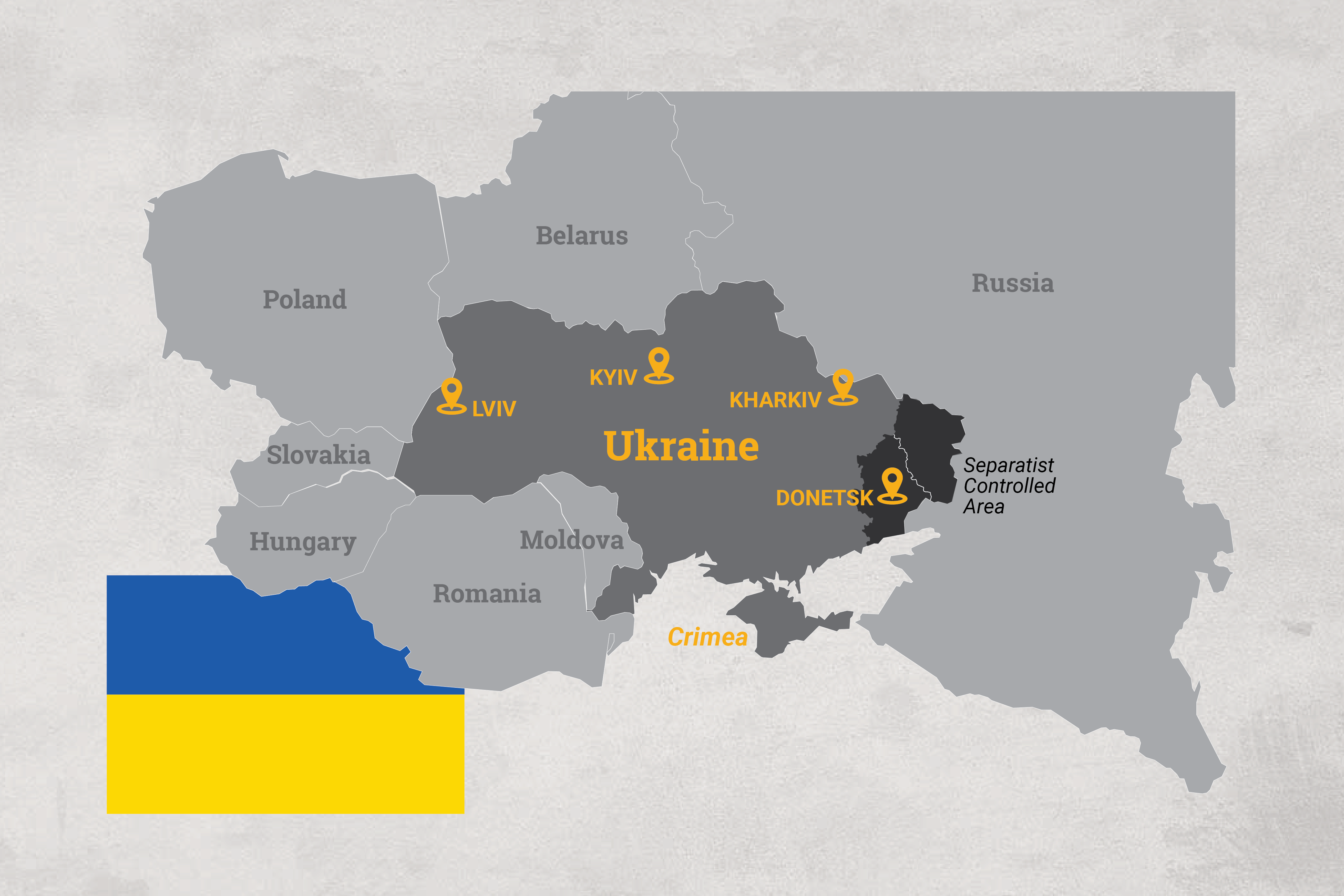
We spoke to people from Donetsk, the capital of the Kremlin-backed separatist Donetsk People’s Republic (DPR); from Kharkiv, a city in eastern Ukraine just 25 miles from the Russian border; from Kyiv, the nation’s capital; and from Lviv, the largest city in western Ukraine, located just 60 miles from the Polish frontier.
Here’s what they said.
“This is not new,” says Daniel Bilak, 61, a Canadian-Ukrainian lawyer and former government adviser who has lived in Ukraine for 30 years. Eight years after Russia’s annexation of Crimea and the start of the separatist conflict in the East, he calls this “just the next phase of the war with Putin.”
According to Bilak, who lives in a small town just outside of Kyiv, people didn’t really start worrying about the recent Russian troop buildup until foreign embassy staffers began leaving last week. That’s when some Kyivans began moving their families to country homes or cities in the west, further from the potential front line.
“As Ukrainians, our philosophy of life is to prepare for the worst and hope for the best,” he says.
As part of that preparation, Bilak and a group of local men his age have been receiving basic military training from a former army major on weekends.
"It's BYOG,” says Bilak, “Bring Your Own Gun.” The Wolverines, as the group calls themselves, could soon become an official volunteer defense unit under a new Ukrainian law.
“It’s a way to channel the anxiety that people have,” Bilak says. “They feel like they have some control over their lives. How effective is that going to be against a platoon of Chechen Spetsnaz [Russian special forces]? I don't know. But if you replicate this in every community, it's not a comfortable place for an invading soldier. And there's a very strong sense that, you know what? We're going to defend this country. Nobody here thinks that this is a suicide mission.”
Marta Spodaryk, 28, a Ph.D. student from Lviv who works in Kyiv, said she was hardly aware of the escalating crisis until the past few days when friends from abroad began writing to ask her about US reports that Russia was set to invade Ukraine.
“I was writing my Ph.D. and didn’t have a chance to follow the news,” she says. “Some people here are like me. They don’t feel anything if they aren’t reading the newspaper articles. Some of those who are are really panicking, moving, packing emergency bags, or buying weapons.”
Spodaryk has made a plan with her brother Vitalii, in Lviv, to leave Kyiv if anything happens and travel as far west as she can to meet him and return to their parents’ home.
The feeling, she says, isn’t so much fear. “It’s more like anger. Not fear. If you are afraid you get messy and you can’t think straight to organize yourself. I feel angry because it’s already eight years of this, and now they are threatening us and a lot of people are panicking. My granny called me today from Lviv and I had to tell her that look, everything is fine, that Kyiv is working perfectly. So it kind of angers me. How dare they do this to us again?”
Her brother, Vitalii Chornenkyi, 32, a trial attorney and law professor at Lviv University, said that although Lviv is far from the potential front line, he and his friends are worried about how far the conflict could spread. Prices for imports and fuel have been rising recently with Ukraine’s currency (the hryvnia) weakening under the threat of war, and he’s noticed that people in more footloose professions like IT have already started preparing to leave.
“I’m scared," he says, “but it’s not the horror movie type of fear. It’s different, a kind of tension, an uncertainty, that your whole life and work could suddenly disappear because of this conflict. We feel like we are just marionettes in other countries’ geopolitical games.”
Every time he hears a plane taking off or landing at a nearby airport, he checks online flight trackers to see where it’s coming from and whom it belongs to. Images of Russia’s devastating air war in Syria, he said, have made him worry about what the Russian military might do to his city.
“It’s strange to talk about fear,” he says. “It’s a common problem with Ukrainians. We talk about the tension in the air, but we don’t communicate about our feelings.”
Further east, in the city of Kharkiv near the Russian border, Roman Danilenkov, co-founder of the independent media organization Nakipelo (“fed up,” in Russian and Ukrainian), says the atmosphere is tense, but mainly among people who follow international news. Others are mostly just going about their lives.
He’s talked to his family about escape plans to Western Ukraine. “It’s scary because we have our whole life here,” he says. “But we have to talk about these things. We have plans in our minds, of course, but we don’t know what’s going to happen.”
And although the conflict has been dragging on for almost a decade now, Danilenkov says that it feels different this time. Not only because of the larger Russian force involved, but also because the Ukrainian army is stronger, better equipped, and more capable. “Still,” he says, “we know that the army of the aggressor is much larger.”
Meanwhile, in separatist-held Donetsk, people’s views of the situation are different. There, says Kateryna Malofieieva, 33, a freelance journalist from Donetsk who covers the conflict from both sides, Russia isn’t seen as a threat. And with few people in the Russian-backed enclave reading western news sources, there is little sense of panic.
What Malofieieva hears about more is simple fatigue with the eight-year-long conflict, and a sense that the current situation is untenable. Living in a territory that is recognized by Russia but isn’t really part of Ukraine, “it’s difficult for people to comprehend who they actually are.” Many in Donetsk, she says, feel that it’s the Ukrainian government that is dragging its feet on a solution.
Whether the current standoff involving Russia, Ukraine, and the West will lead to a durable resolution remains anyone’s guess. Ukrainians are dealing with the tension in myriad ways, but those who spoke with GZERO seemed to agree on one thing: enough is enough.