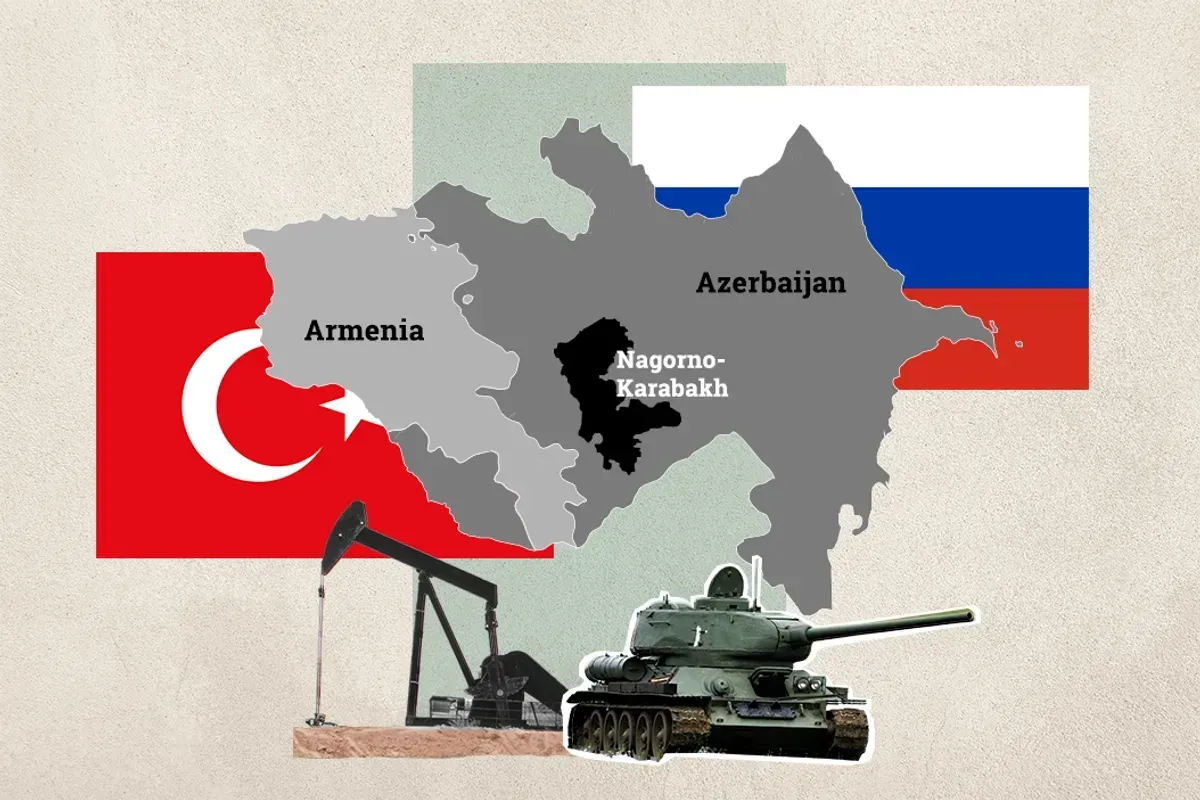
The long-simmering conflict in Nagorno-Karabakh has once again heated up, with Armenia accusing Azerbaijan of blocking the only road that connects the disputed region with Armenia.
The Azeris, of course, deny this and blame Russian peacekeepers. But what's clear is that the longer the area remains cut off from Armenian supplies, the higher the risk of a humanitarian crisis in a land that's been embroiled in an unresolved conflict for decades.
The context. Armenia and Azerbaijan went to war for the rugged highlands of Nagorno-Karabakh alongside the collapse of the Soviet Union. The area was part of the Azerbaijan Soviet Republic, but the national awakenings of the Gorbachev era sparked the movement in the region to join Armenia.
The war ended in 1994 with a fragile truce that left Nagorno-Karabakh as a de-facto protectorate of Armenia, only recognized by Yerevan. Periodic clashes have persisted since then, during which time Azerbaijan invested its growing oil wealth into a modern military. In 2020, a second all-out war erupted for six weeks, leaving Azerbaijan in control of most of the enclave.
(For more, including relevant outside players, check our primer here.)
On the Armenian side, the biggest worry is what’ll happen to the 120,000 residents of Artsakh — as Yerevan, the Armenian capital, calls Nagorno-Karabakh — if the blockade continues.
"It's like West Berlin," Ruben Vardanyan, a Russian-Armenian billionaire and philanthropist who was recently appointed state minister by the self-proclaimed government of Artsakh, tells Ian Bremmer in an interview from the capital, Stepanakert. Azerbaijan, he says, can't have it both ways: If you want us to be citizens, you must let us live a normal life.
"We need to find a way to live together like neighbors, not together from [the same] country, but [as] neighbors who need to accept each other, and not hate each other, and not kill each other," he says. "We will not live together like one state, but we can live together in one region because we've been living close to each other [for] hundreds of years."
Meanwhile, Azerbaijan sees the situation very differently. For Baku, the second war actualized their longstanding claim to the territory. And the ongoing blockade is part of a pattern following the 2020 cease-fire, in which Azerbaijan is pushing the facts on the ground in its favor.
Azerbaijan and Armenia are, in fact, negotiating a peace agreement that in theory can offer the chance to move past the conflict. As Russia reportedly prepares to host another round of talks this month, Yerevan might be willing to recognize Azerbaijan’s territorial claims in exchange for some special status for those parts of Karabakh still under Armenian control.
But local officials in Stepanakert have chafed at the negotiations. With steps like the blockade, Baku might be trying to show its leverage to pressure an outcome in its favor.
Another big piece of this geopolitical puzzle is the presence of Russian peacekeepers as part of the 2020 cease-fire agreement. The Azeris, who are backed in the conflict by Turkey but have working ties with Russia, now see that the geopolitical environment has shifted in their favor with Russian forces tied up in Ukraine.
Russia technically has a defense treaty with Armenia, but Moscow made it clear in 2020 that did not apply to Nagorno-Karabakh. With Europe also turning to Azerbaijan for more oil and natural gas as it reduces Russian imports, Baku might find supporters abroad even if it tightens the screws in the disputed region.
For Armenia, Russia’s unwillingness to stand up for its ally is proving to be a headache. But both Yerevan and Stepanakert will still expect Russia to be at the table as part of any deal. Vardanyan would like Moscow to deploy more peacekeepers and have them stay longer.
Whatever the future holds for Nagorno-Karabakh, things are not looking good. Azerbaijan has little incentive to back down, Armenia's best friend won't get involved, and Western powers have yet to offer major incentives for an equitable agreement.
The war over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been forgotten. But for much of the West, it is worth asking if it will be a priority.
- Special podcast: View from "fully blockaded" Nagorno-Karabakh during Armenia's conflict with Azerbaijan - GZERO Media ›
- Armenia, Azerbaijan & the Nagorno-Karabakh crisis that needs attention - GZERO Media ›
- Armenia’s capital reels from the aftermath of Nagorno-Karabakh & Russia-Ukraine wars - GZERO Media ›
- Overlooked stories in 2023 - GZERO Media ›