What We're Watching: Africa's vaccine shortage, Colombian unrest, Bibi fails to form government
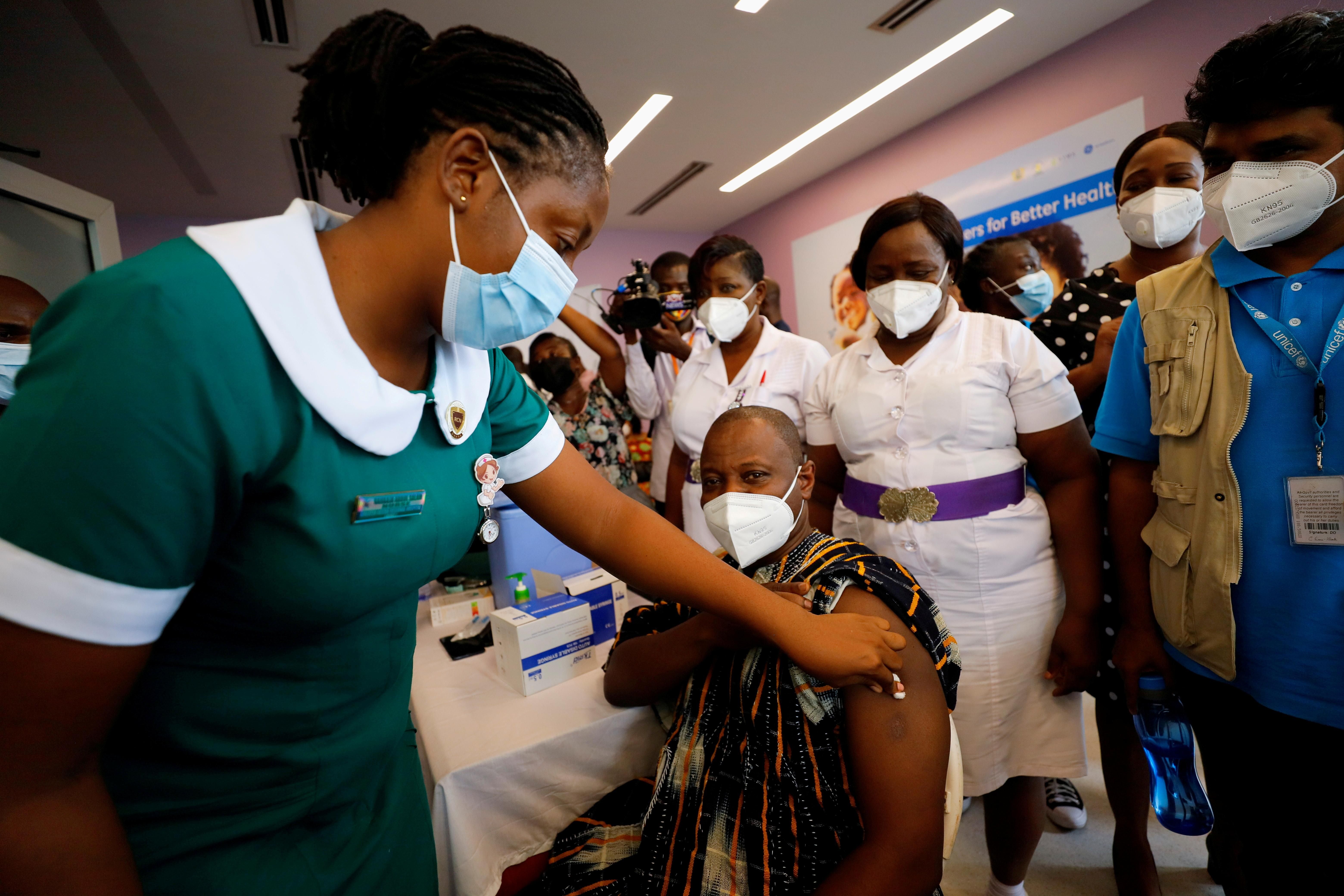
India's COVID crisis hurts Africa: As COVID started to ravage India in March, New Delhi announced a ban on all vaccine exports to prioritize the domestic crisis. This development was a massive blow for the COVAX facility, which is relying on India's Serum Institute manufacturing the AstraZeneca shot for low-income countries. The impact of this export ban is now being felt acutely across Africa, where many countries have received a scarce number of doses. The World Health Organization says that at least seven African countries including Rwanda, Ghana, and Senegal have already exhausted all their vaccine supplies — and because of delays from India, will now need to wait several weeks for more to arrive. COVAX, which has received 90 million fewer doses to date than it was initially promised, says it needs an extra 20 million doses by the end of June to offset shortfalls caused by the worsening crisis in India. It's a worrying trend: while inoculation drives in places like the US, the UK and Israel are allowing their economies to reopen and life to slowly return to normal, many low-income countries will not return to normalcy for years, experts warn. To date, only 2 percent of all doses administered globally have been in Africa, despite the continent accounting for 17 percent of the global population.
Colombian unrest over tax reform: The UN has called out Colombia for using excessive force to disperse recent street protests against the government's planned tax hikes, which left at least 19 people dead in Cali, the country's third largest city. The protesters wanted President Iván Duque to withdraw his controversial proposal to raise taxes for the middle class, which Duque says is needed in order to raise revenue to help the Colombian economy recover from the pandemic. But the backlash against his measures was so strong that the government quickly relented. The fact that Duque caved after just a few days of rallies underscores how unpopular his proposed reforms are, and will likely limit his government's ability to cut back on any social spending before his term ends next year. Whoever takes over from Duque will now have to deal with a sizable hole in Colombia's finances, and the economy could become a big campaign issue in the 2022 presidential election — in which the frontrunner is now Gustavo Petro, the big-spending former mayor of the capital Bogotá.
Israel's political stalemate persists: Four weeks after Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu's Likud party won the most seats in parliamentary elections — and was then tapped by President Reuven Rivlin to try and form a coalition government — Israel's political stalemate continues. After Bibi has failed again to bring enough parties together to form a workable coalition, there are several potential scenarios for how this could all play out. Rivlin could ask Yesh Atid (There is a Future) leader Yair Lapid, who heads the anti-Bibi opposition bloc and came in second in the March vote, to try and reach a 61-seat majority. Israeli media report that this is the most likely scenario, though it won't be an easy feat for Lapid amid Israel's deeply divided political milieu. Rivlin could also throw the mandate to Naftali Bennett, a former Netanyahu ally who leads a small right-wing party but whose support both sides need to form a government. Center left-leaning Lapid and Bennett might try to work together to oust Netanyahu, but ideological differences would likely undermine that effort. Both politicians say they are committed to doing whatever it takes to avoid another election, which would be Israel's fifth since April 2019. But if the current political stalemate persists, that's exactly where this is all heading.