Analysis
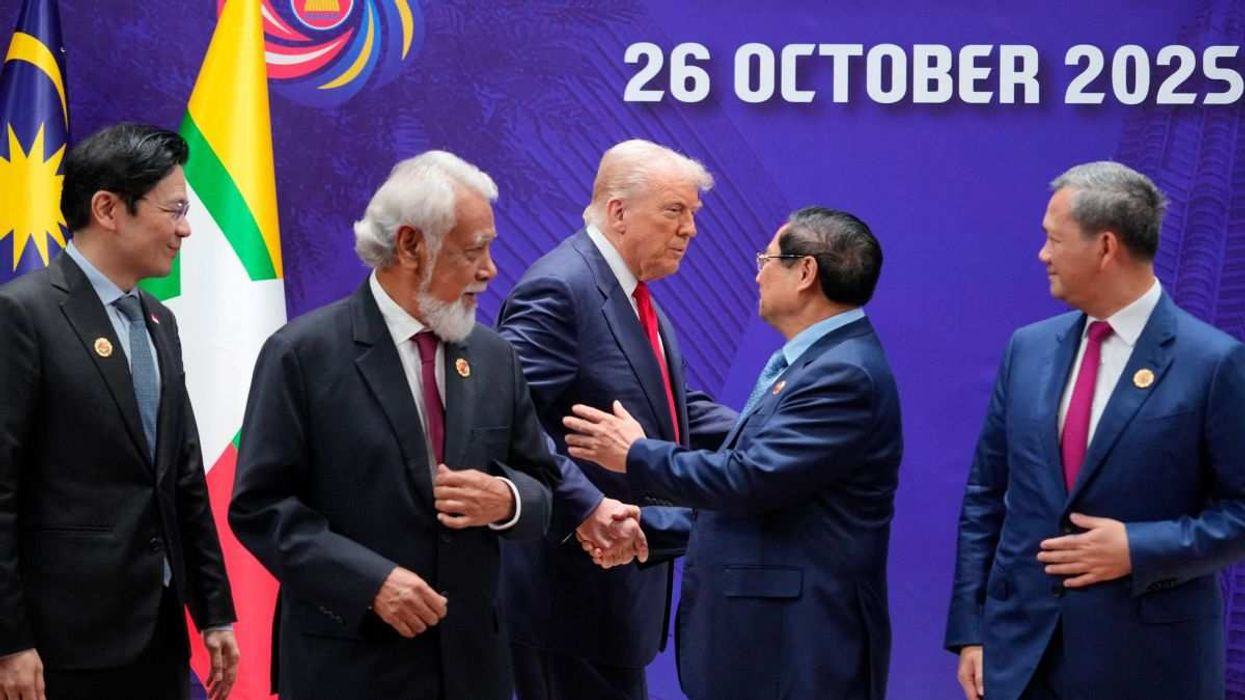
Trump’s Asian trade blitz sets up sitdown with Xi
The US president signed a raft of trade deals on Sunday at the ASEAN summit in Malaysia, but the main event of his Asia trip will be his meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping on Thursday.
Oct 27, 2025