News
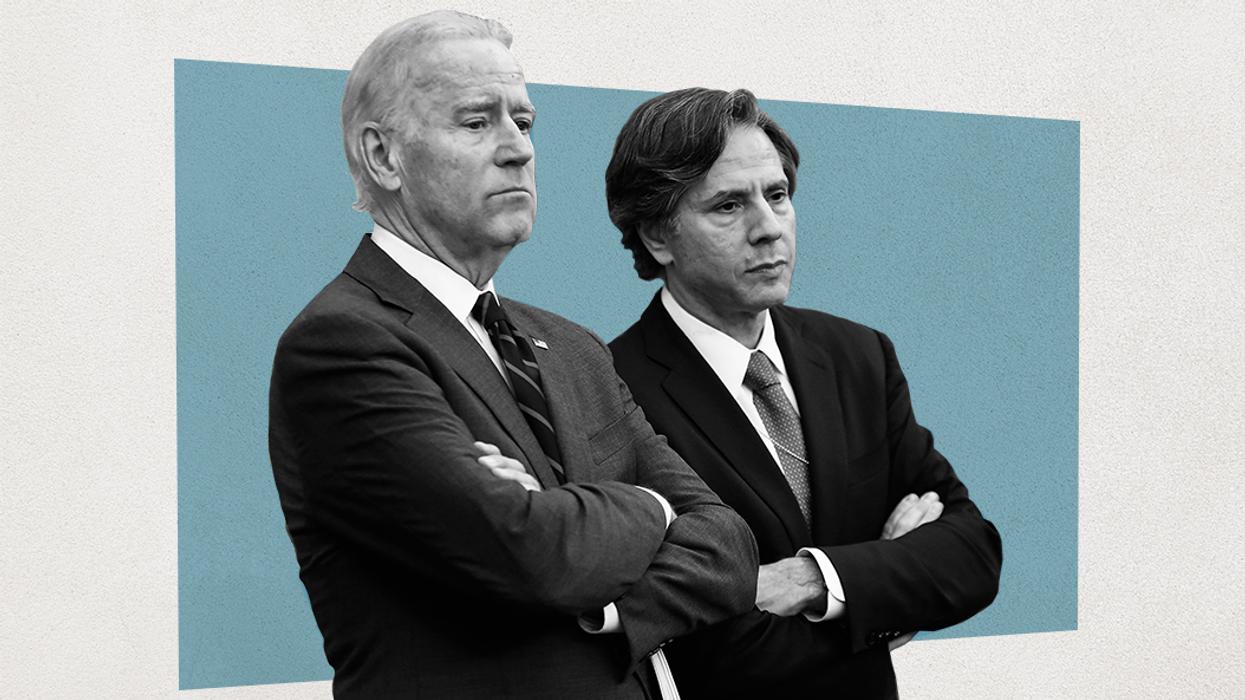
Who is Tony Blinken?
The person a US president taps to assume the coveted role of secretary of state, the nation's top diplomat, says a lot about that president's foreign policy ambitions and global vision. Biden has now tapped Tony Blinken to head the State Department. What does that tell us?
Nov 23, 2020