News
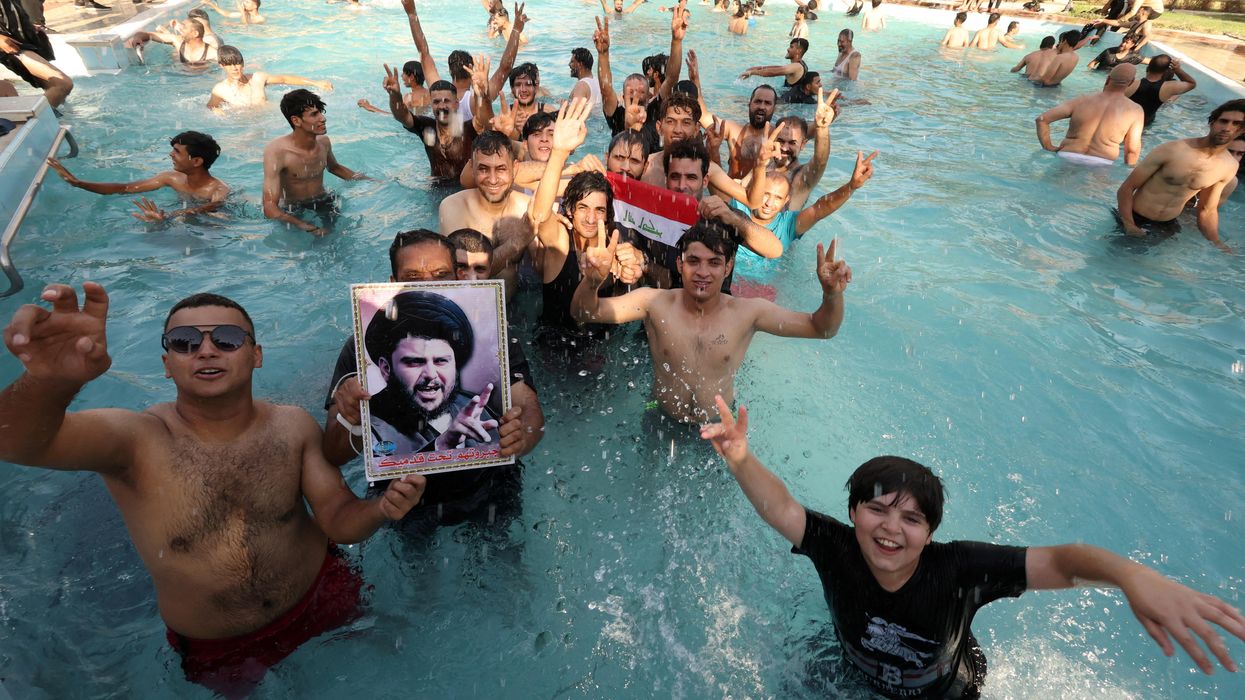
What We're Watching: Deadly clashes in Iraq, China-Russia military drills, Colombia-Venezuela restore ties
Three big stories we're watching today: Political chaos and deadly clashes in Iraq, China-Russia military drills in Russia's far east, Colombia-Venezuela restore ties after three years.
Aug 29, 2022