GZERO World Clips
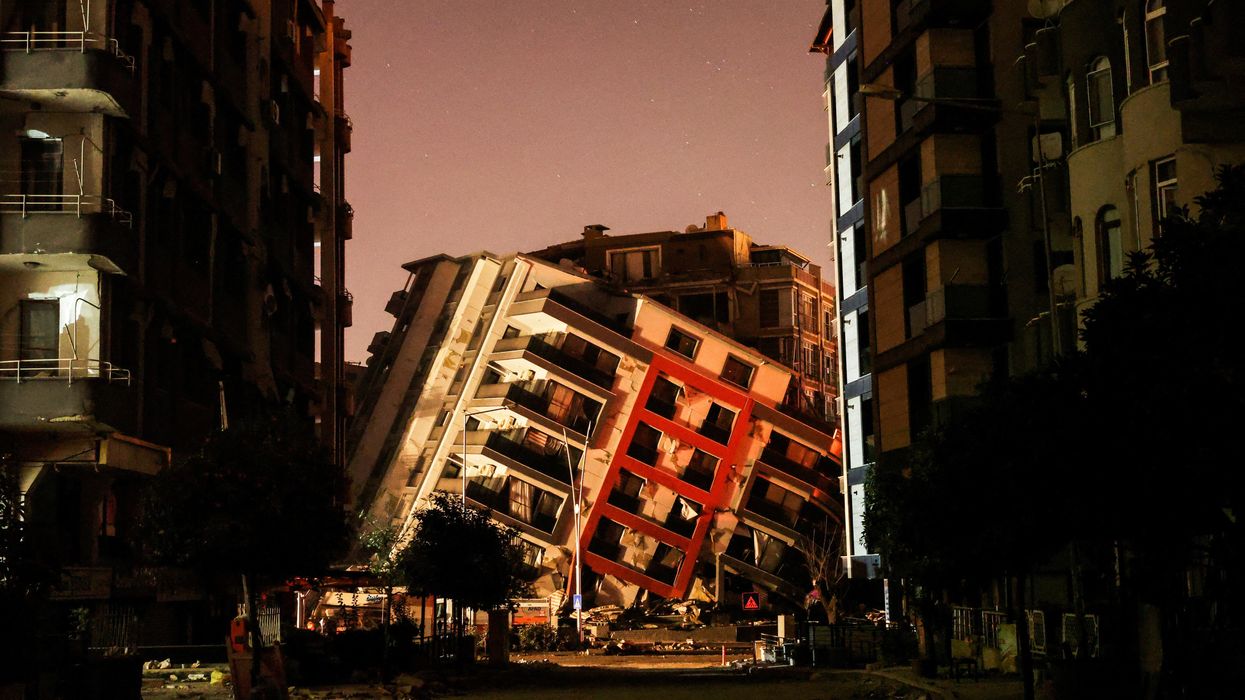
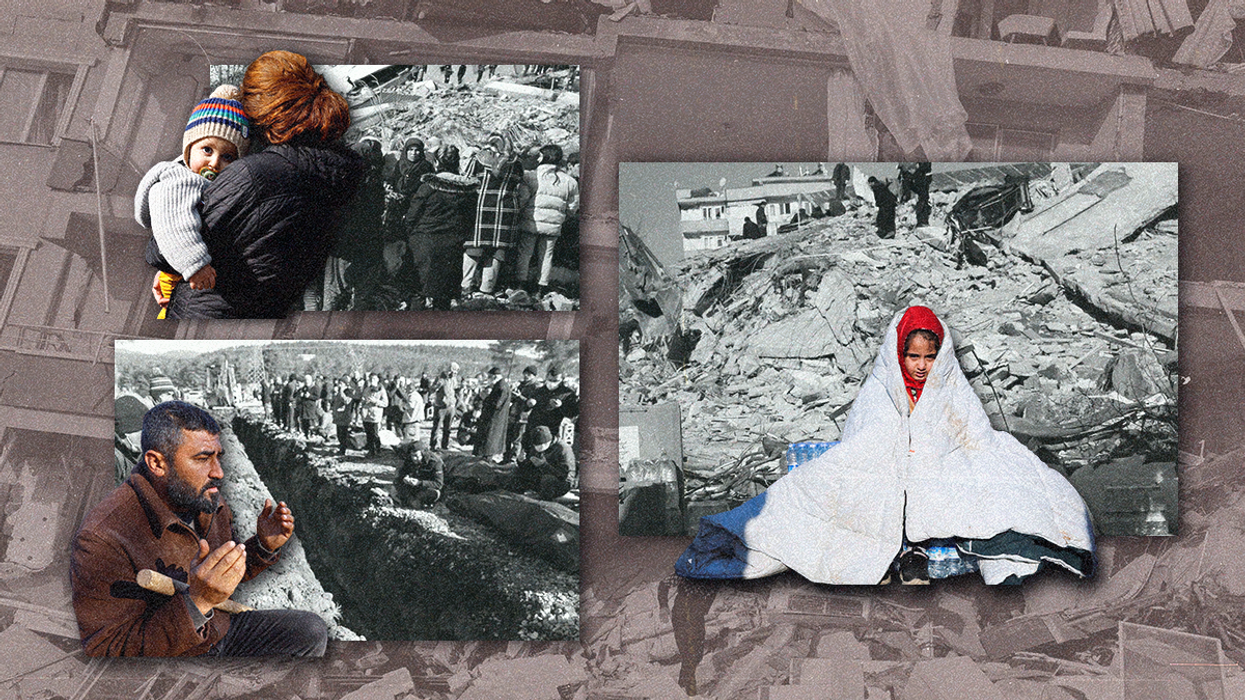
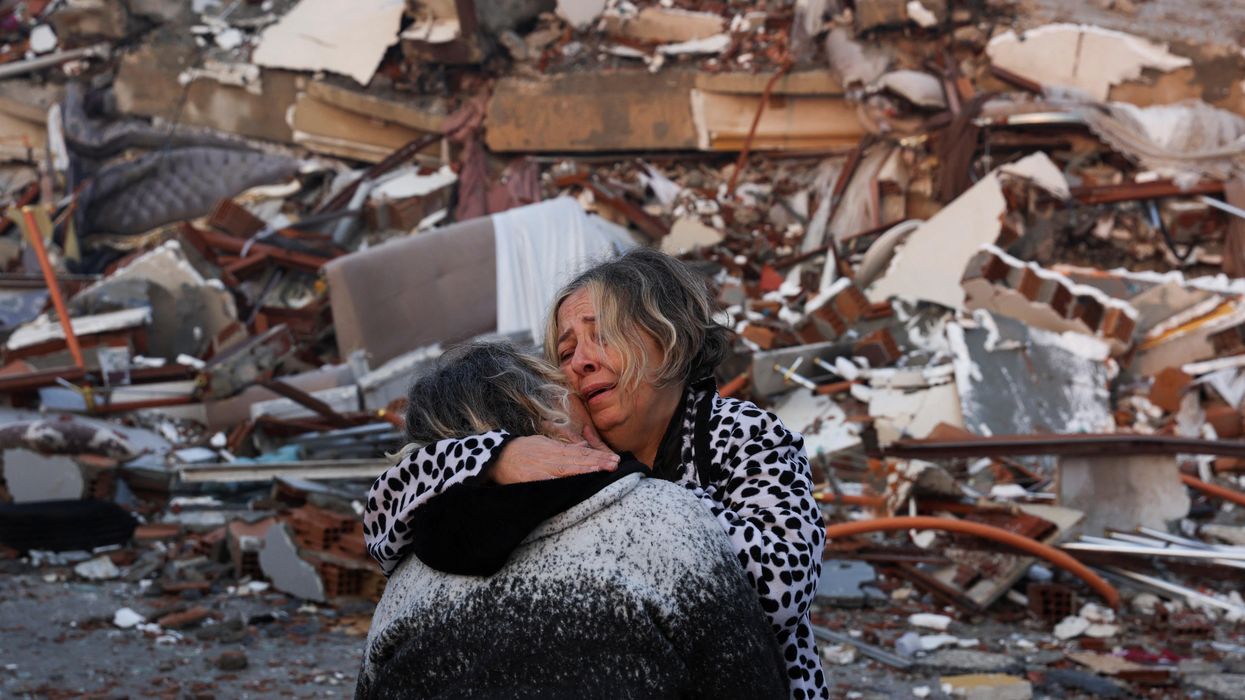
Earthquakes expose political and humanitarian challenges in Turkey and Syria
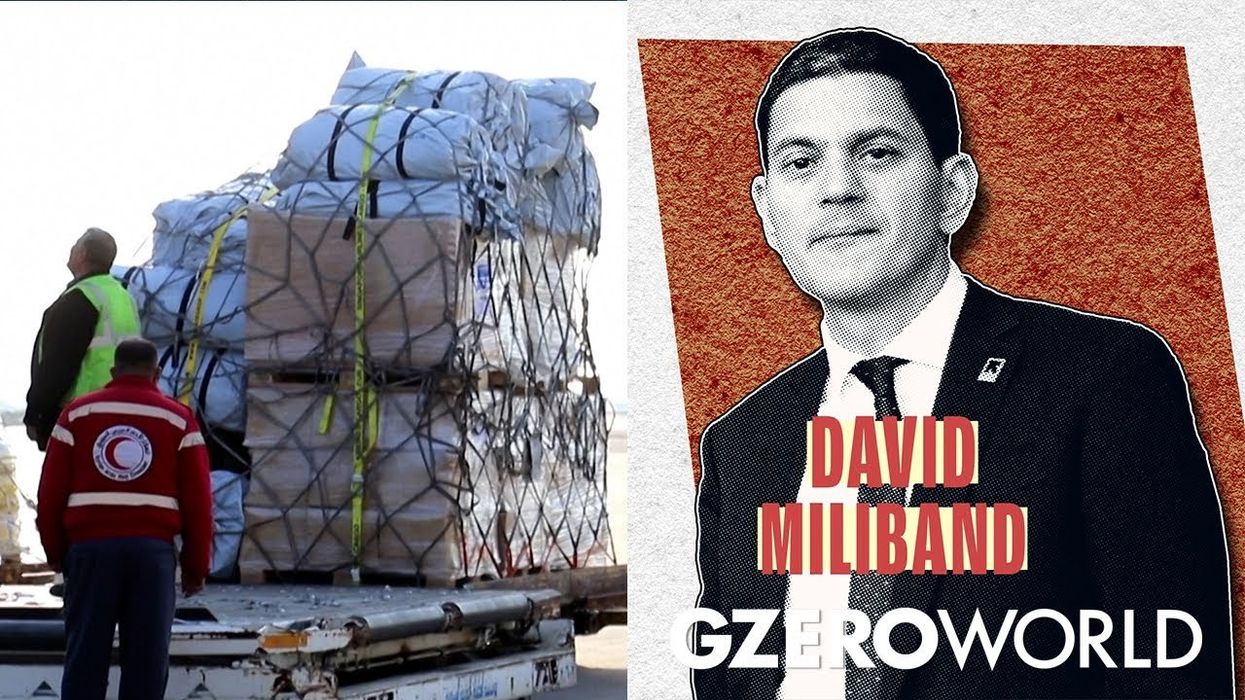
In a recent episode of GZERO World, the International Rescue Committee's President and CEO, David Miliband, sheds light on the immense challenges of delivering aid in the aftermath of the deadly earthquakes that rocked Turkey and Syria. With the northwest of Syria controlled by armed opposition groups, aid delivery remains a hurdle that needs to be overcome urgently.
Mar 26, 2023