Load More
VIDEOSGZERO World with Ian BremmerQuick TakePUPPET REGIMEIan ExplainsGZERO ReportsAsk IanGlobal Stage
Site Navigation
Search
Human content,
AI powered search.
Latest Stories
Start your day right!
Get latest updates and insights delivered to your inbox.
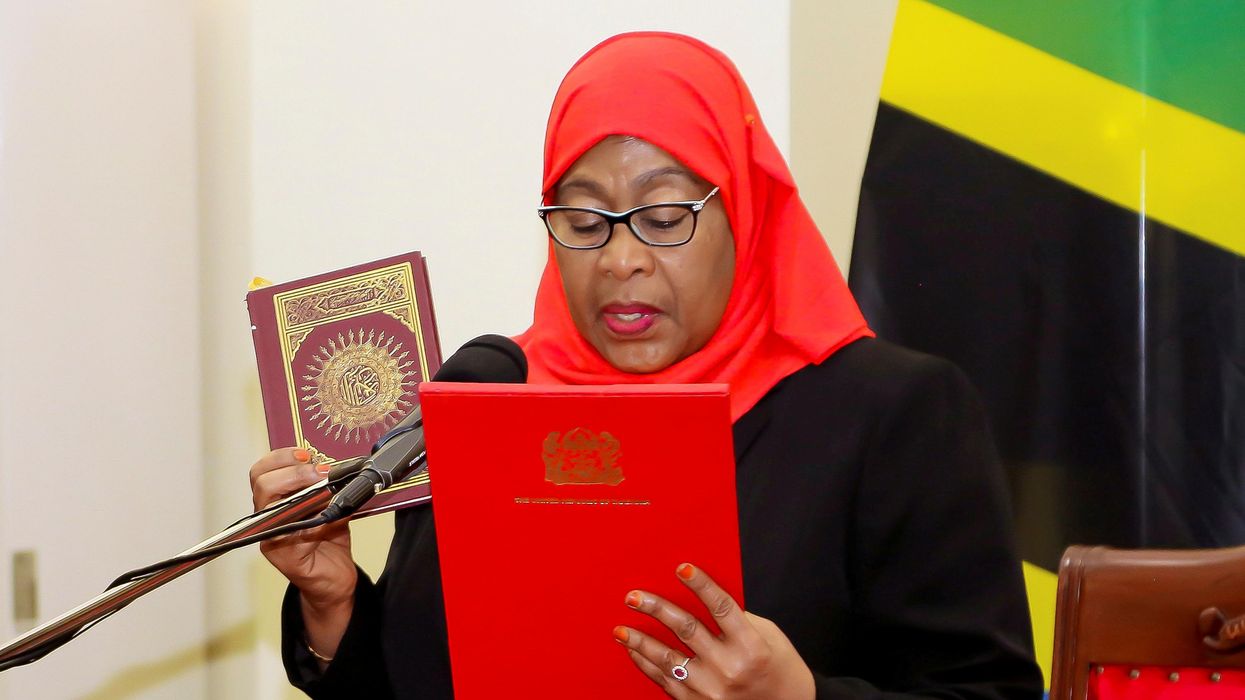
tanzania
GZERO Daily: our free newsletter about global politics
Keep up with what’s going on around the world - and why it matters.