September 28, 2020
The long-simmering conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over a region called Nagorno-Karabakh erupted over the weekend, with more than 50 killed (so far) in the fiercest fighting in years. Will it escalate into an all-out war that threatens regional stability and drags in major outside players?
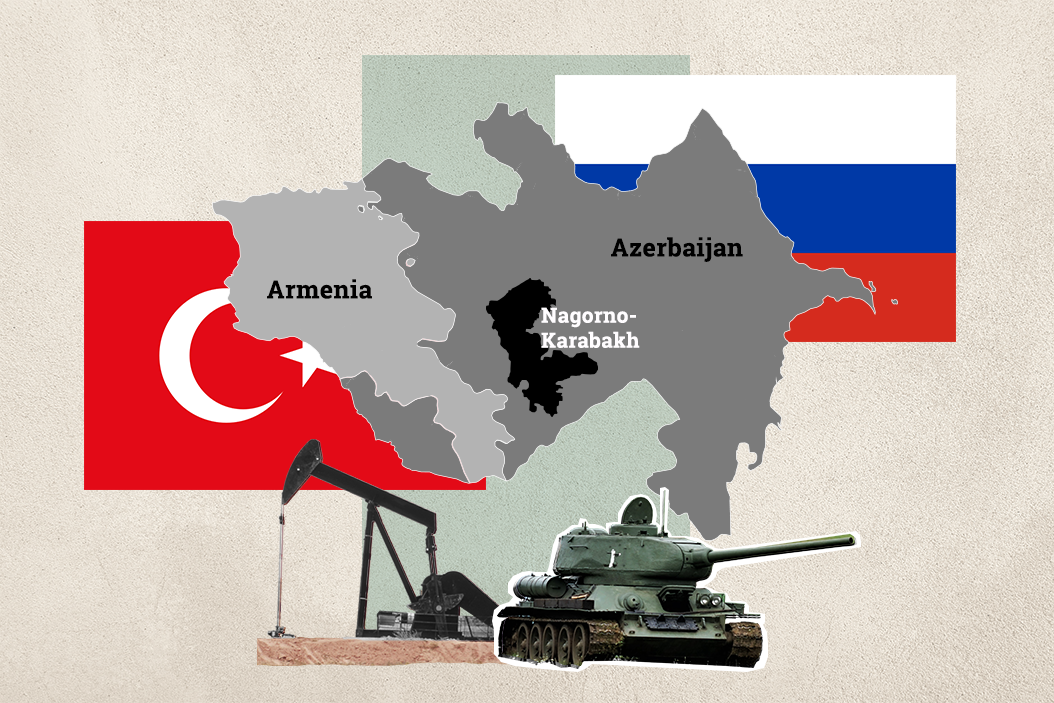
What's the background? For years, Armenia and Azerbaijan have been at odds over the rugged highlands of Nagorno-Karabakh. In the dying days of the USSR, the two sides fought a bloody six-year war to control the enclave, which was part of Muslim-majority Azerbaijan but mainly populated by ethnic Armenian Christians.
The conflict ended in 1994 with over 30,000 dead, more than one million displaced, and a fragile truce that left Nagorno-Karabakh as a de facto independent state, supported by Armenia but not recognized by other countries, including Azerbaijan. Low-level clashes have persisted ever since — including deadly skirmishes in 2016 — and both governments often use the conflict to stoke nationalist flames at home.
Although the trigger for the latest violence is still unclear, bilateral tensions have been rising since mid-July, when 16 soldiers died in border clashes. That violence sparked an uproar in Azerbaijan, where thousands of Azeris took to the streets calling for the army to "recapture" Nagorno-Karabakh. Now, both sides are accusing each other of throwing the first punch, and have declared martial law.
A war over the enclave would resonate far beyond the region. The South Caucasus, where Armenia and Azerbaijan are located, has enormous strategic importance because it is crossed by two major energy pipelines that carry Azeri oil and Caspian Sea gas to Turkey and Europe.
Two outside players — Turkey and Russia — are on opposite sides of the conflict. Turkey has close relations with fellow Turkic Azerbaijan, and historically there is little love lost between Ankara and the Armenians. Moreover, Azerbaijan is Turkey's main oil supplier. Turkey has denied reports that it has sent 4,000 Syrians to fight on behalf of the Azeri army, but Turkish President Recep Erdogan's moves here merit close attention.
Russia is the dominant player in the region. But although it sells weapons to both Azerbaijan and Armenia, Moscow keeps troops garrisoned in Armenia and is, technically, treaty-bound to defend the country. If things escalate further, Vladimir Putin will have to decide whether to honor that obligation. Doing so could quickly put Ankara and Moscow on opposite sides of another nasty war (they already back different sides of the civil war in Libya.)
Finally, Iran also has a stake. It borders both countries, and Azeris are Iran's largest ethnic minority. Although Tehran has traditionally backed Yerevan, and often bickers with Baku over energy and security in the Caspian Sea, the Iranians offered to mediate when the latest tensions began two months ago. Will they try again now?
More For You
- YouTube
In this Quick Take, Ian Bremmer examines the second week of the US-Israel war with Iran and warns that the conflict risks spiraling into a longer and more destabilizing situation.
Most Popular
- YouTube
What might Iran look like a year from now? Ian Bremmer and Brooking’s Thomas Wright discuss possible outcomes.
Smoke rises after an Israeli strike on Beirut's southern suburbs, following an escalation between Hezbollah and Israel amid the US-Israeli conflict with Iran, on March 6, 2026.
REUTERS/Khalil Ashawi
The Lebanese militant group’s strikes against Israel on Monday appear to have given the Israelis the pretext to launch a massive counter-attack, with the ultimate aim being to disarm the Iran-backed group once and for all.
Iran conflict fueled food crisis, Rapper set to win in Nepal, US gives Russia sanction relief
Mar 06, 2026
Cargo ships are unloading newly arrived chemical fertilizers at the port terminal in Lianyungang, East China's Jiangsu province, on February 27, 2024.
(Photo by Costfoto/NurPhoto)
Disruptions to a key Gulf waterway in the Iran conflict aren't just threatening the world’s oil and gas supplies; they could also cause a food security crisis.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.